Isolated Nocturnal Hypertension in Children
- PMID: 35252065
- PMCID: PMC8894436
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.823414
Isolated Nocturnal Hypertension in Children
Abstract
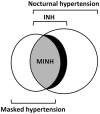
Isolated nocturnal hypertension (INH) is attracting attention because it has been shown to correlate with target organ damage as well as cardiovascular events in adults. INH has also been reported in children especially in those with underlying diseases including chronic kidney disease and some studies reported association with markers of early target organ damage. INH occupies the majority of nocturnal hypertension. On the other hand, masked hypertension is largely attributed to INH. INH is usually diagnosed by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Recently, it became possible to monitor sleep blood pressure by an automated home blood pressure device feasible also in children. The epidemiology, methodology and reproducibility, pathophysiology, relation to target organ damage, and treatment of INH in children will be reviewed here along with adult data.
Keywords: children; clinic blood pressure; isolated nocturnal hypertension; masked hypertension; masked isolated nocturnal hypertension; target organ damage.
Copyright © 2022 Awazu.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. . 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2018) 138:e426–83. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000597 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

