Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio in Predicting Long-Term Mortality in Patients Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: An Analysis of the MIMIC-III Database
- PMID: 35252328
- PMCID: PMC8894887
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.801708
Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio in Predicting Long-Term Mortality in Patients Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: An Analysis of the MIMIC-III Database
Abstract
Background: This study examined the role of blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio (BAR) in predicting long-term mortality in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, patients undergoing CABG were enrolled from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC III) database. Patients were divided into the three groups according to the optimal cutoff values of BAR determined by X-tile software. The survival curve was constructed by the Kaplan-Meier method and multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to explore the independent prognostic factors of 1- and 4-year mortality after CABG. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) were calculated to estimate the accuracy of BAR in predicting the outcomes. Subgroup analyses were also carried out.
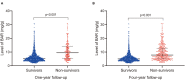
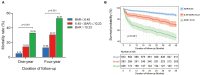
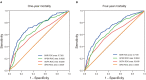
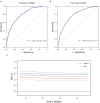
Results: A total of 1,462 patients at 4-year follow-up were included, of which 933, 293, and 236 patients were categorized into the group 1 (≤ 6.45 mg/g), group 2 (>6.45 and ≤ 10.23 mg/g), and group 3 (>10.23 mg/g), respectively. Non-survivors showed an increased level of BAR at both 1- (p < 0.001) and 4-year (p < 0.001) follow-up compared with the survivors. The patients with a higher BAR had a higher risk of 1- and 4-year mortality following CABG (33.05 vs. 14.33 vs. 5.14%, p < 0.001 and 52.97 vs. 30.72 vs. 13.08%, p < 0.001, respectively). Cox proportional hazards regression model suggested a higher BAR as an independent risk factor of 1-year mortality (HR 3.904; 95% CI 2.559-5.956; P < 0.001) and 4-year mortality (HR 2.895; 95% CI 2.138-3.921; P < 0.001) after adjusting for confounders. Besides, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves showed the better predictive ability of BAR compared to other grading scores at both 1- (0.7383, 95% CI: 0.6966-0.7800) and 4-year mortality (0.7189, 95% CI: 0.6872-0.7506). Subgroup analysis demonstrated no heterogeneous results of BAR in 4-year mortality in particular groups of patient.
Conclusion: This report provided evidence of an independent association between 1- and 4-year mortality after CABG and BAR. A higher BAR was associated with a higher risk of long-term mortality and could serve as a prognostic predictor in patients following CABG.
Keywords: MIMIC III database; albumin; blood urea nitrogen; coronary artery bypass grafting; mortality.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Chen, Liu, Xu, Shen, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Zou and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predictive Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Long-Term Mortality in Intensive Care Unit Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Mar 1;15:2247-2259. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S349722. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35256854 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the value of blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio in patients with acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit: a retrospective cohort study.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 16;12:1435356. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1435356. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40308642 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum anion gap and risk of long-term mortality in patients following coronary artery bypass grafting: A propensity score matching study.J Card Surg. 2022 Dec;37(12):4906-4918. doi: 10.1111/jocs.17167. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Card Surg. 2022. PMID: 36378900
-
Stroke Rates Following Surgical Versus Percutaneous Coronary Revascularization.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Jul 24;72(4):386-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.04.071. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30025574
-
Performance of EuroSCORE in CABG and off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: single institution experience and meta-analysis.Eur Heart J. 2009 Feb;30(3):297-304. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn581. Epub 2009 Jan 13. Eur Heart J. 2009. PMID: 19141560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Prognostic Value of 10 Biochemical Indices at Admission for Prediction Postoperative Myocardial Injury and Hospital Mortality in Patients with Osteoporotic Hip Fracture.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 16;11(22):6784. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226784. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431261 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and prediction model for mortality in HIV/Talaromyces marneffei co-infection: A retrospective cohort study.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 6;10(11):e32560. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32560. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38961941 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio and Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 27;7(8):150. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7080150. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36006242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between early blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio and one-year post-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: a propensity score-matched study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Jul 21;23(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02212-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37479965 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;11(1):49. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11010049. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nawrocki MJ, Perek B, Sujka-Kordowska P, Konwerska A, Kałuzna S, Zawierucha P, et al. . Differences in expression of genes involved in bone development and morphogenesis in the walls of internal thoracic artery and saphenous vein conduits may provide markers useful for evaluation graft patency. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:4890. 10.3390/ijms20194890 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zarei M, Najafi M, Movahedi E, Javanbakht MH, Choi Y-H, Yaseri M, et al. . The predictive role of circulating telomerase and vitamin D for long-term survival in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery (CABG). PloS ONE. (2020) 15:e0237477. 10.1371/journal.pone.0237477 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

