Using a Systems Approach to Explore the Mechanisms of Interaction Between Severe Covid-19 and Its Coronary Heart Disease Complications
- PMID: 35252372
- PMCID: PMC8888693
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.737592
Using a Systems Approach to Explore the Mechanisms of Interaction Between Severe Covid-19 and Its Coronary Heart Disease Complications
Abstract
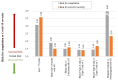
Frontiers requested research on how a systems approach can explore the mechanisms of cardiovascular complications in Covid-19. The focus of this paper will thus be on these detailed mechanisms. It will elucidate the integrated pathogenic pathways based on an extensive review of literature. Many severe Covid-19 cases and deaths occur in patients with chronic cardiovascular comorbidities. To help understand all the mechanisms of this interaction, Covid-19 complications were integrated into a pre-existing systems-based coronary heart disease (CHD) model. Such a complete model could not be found in literature. A fully integrative view could be valuable in identifying new pharmaceutical interventions, help understand how health factors influence Covid-19 severity and give a fully integrated explanation for the Covid-19 death spiral phenomenon seen in some patients. Covid-19 data showed that CHD hallmarks namely, Hypercoagulability, Hypercholesterolemia, Hyperglycemia/Hyperinsulinemia, Inflammation and Hypertension have an important effect on disease severity. The pathogenic pathways that Covid-19 activate in CHD were integrated into the CHD model. This fully integrated model presents a visual explanation of the mechanism of interaction between CHD and Covid-19 complications. This includes a detailed integrated explanation of the death spiral as a result of interactions between Inflammation, endothelial cell injury, Hypercoagulability and hypoxia. Additionally, the model presents the aggravation of this death spiral through the other CHD hallmarks namely, Hyperglycemia/Hyperinsulinemia, Hypercholesterolemia, and/or Hypertension. The resulting model further suggests systematically how the pathogenesis of nine health factors (stress, exercise, smoking, etc.) and seven pharmaceutical interventions (statins, salicylates, thrombin inhibitors, etc.) may either aggravate or suppress Covid-19 severity. A strong association between CHD and Covid-19 for all the investigated health factors and pharmaceutical interventions, except for β-blockers, was found. It is further discussed how the proposed model can be extended in future to do computational analysis to help assess the risk of Covid-19 in cardiovascular disease. With insight gained from this study, recommendations are made for future research in potential new pharmacotherapeutics. These recommendations could also be beneficial for cardiovascular disease, which killed five times more people in the past year than Covid-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cardiovascular comorbidities; coronary heart disease; systems-approaches.
Copyright © 2022 Meyer, Mathews, Gous and Mathews.
Conflict of interest statement
This study received funding from HumanSim (Pty) Ltd. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis,interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
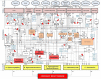
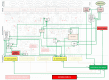
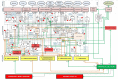
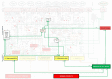
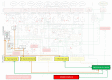
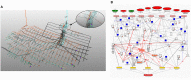
 ). The blunted blue arrows denote antagonize or inhibit and pointed blue arrows denote up-regulate or facilitate. ACE, angiotensin-converting-enzyme; β-blocker, beta-adrenergic antagonists; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; OX, cyclooxygenase; CRP, C-reactive protein; D-dimer, fibrin degradation product D; FFA, free fatty acids; GCF, gingival crevicular fluid; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin A1c; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; Hs, homocysteine; ICAM, intracellular adhesion molecule; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IL, interleukin; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NFκβ, nuclear factor-κβ; NLRP3, Inflammasome responsible for activation of inflammatory processes as well as epithelial cell regeneration and microflora; NO, nitric oxide; NO-NSAIDs, combinational NO-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; OPG, osteoprotegerin; oxLDL, oxidized LDL; PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; P. gingivalis, Porphyromonas gingivalis; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-beta ligand; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCD-40, recombinant human sCD40 ligand; SMC, smooth muscle cell; SSRI, serotonin reuptake inhibitors; TF, tissue factor; TMAO, an oxidation product of trimethylamine (TMA); TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
). The blunted blue arrows denote antagonize or inhibit and pointed blue arrows denote up-regulate or facilitate. ACE, angiotensin-converting-enzyme; β-blocker, beta-adrenergic antagonists; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; OX, cyclooxygenase; CRP, C-reactive protein; D-dimer, fibrin degradation product D; FFA, free fatty acids; GCF, gingival crevicular fluid; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin A1c; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; Hs, homocysteine; ICAM, intracellular adhesion molecule; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IL, interleukin; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NFκβ, nuclear factor-κβ; NLRP3, Inflammasome responsible for activation of inflammatory processes as well as epithelial cell regeneration and microflora; NO, nitric oxide; NO-NSAIDs, combinational NO-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; OPG, osteoprotegerin; oxLDL, oxidized LDL; PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; P. gingivalis, Porphyromonas gingivalis; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-beta ligand; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCD-40, recombinant human sCD40 ligand; SMC, smooth muscle cell; SSRI, serotonin reuptake inhibitors; TF, tissue factor; TMAO, an oxidation product of trimethylamine (TMA); TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; vWF, von Willebrand factor.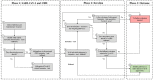


Similar articles
-
The Impact of COVID-19 On Comorbidities: A Review Of Recent Updates For Combating It.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 May;29(5):3586-3599. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35165505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do high glycemic load diets influence coronary heart disease?Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015 Mar 8;12:6. doi: 10.1186/s12986-015-0001-x. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25774201 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP): An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(5):1-70. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074496 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics and system biology approach to identify the influences of COVID-19 on cardiovascular and hypertensive comorbidities.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Mar 22;22(2):1387-1401. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa426. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33458761 Free PMC article.
-
The integrated effect of moderate exercise on coronary heart disease.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2017 Mar/Apr 23;28(2):125-133. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2016-058. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2017. PMID: 27942693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 - 10 August 2021 (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on... (accessed August 10, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

