A novel method of transvesicoscopic ureteral reimplantation of an ectopic ureter with a mate ureter in a duplex kidney
- PMID: 35252800
- PMCID: PMC8888004
- DOI: 10.1002/iju5.12401
A novel method of transvesicoscopic ureteral reimplantation of an ectopic ureter with a mate ureter in a duplex kidney
Abstract
Introduction: The reimplantation of an ectopic ureter is still performed as an open surgery, although laparoscopic or robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery has gained popularity as a minimally invasive treatment for pediatric urological disorders.
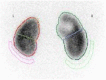
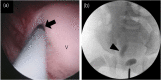
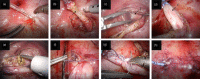
Case presentation: A 15-day-old Japanese boy was referred to our hospital with right hydronephrosis. A detailed examination revealed complete ureteral duplication on the right side and a dilated ectopic upper pole ureter, opening into the prostatic urethra. Since the patient had recurrent febrile urinary tract infections, we performed plication and ureteral reimplantation of the dilated ectopic ureter using a transvesicoscopic surgical method at the age of 2 years and 5 months.
Conclusion: We safely performed transvesicoscopic ureteral reimplantation for an ectopic upper pole ureter with a mate ureter in a duplex kidney, following the detection of an ectopic ureter within the bladder, due to the prior understanding of the wrapping of both ureters in a common sheath.
Keywords: common sheath; duplex kidney; ectopic ureter; transvesicoscopic ureteral reimplantation; ureteroplasty.
© 2021 The Authors. IJU Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kutikov A, Nguyen M, Guzzo T, Canter D, Casale P. Laparoscopic and robotic complex upper‐tract reconstruction in children with a duplex collecting system. J. Endourol. 2007; 21: 621–4. - PubMed
-
- Herz D, Smith J, McLeod D, Schober M, Preece J, Merguerian P. Robot‐assisted laparoscopic management of duplex renal anomaly: comparison of surgical outcomes to traditional pure laparoscopic and open surgery. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2016; 12: e1–7. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez MV, Boysen WR, Gundeti MS. Robot‐assisted laparoscopic common sheath ureteral reimplantation in duplex ureters: LUAA technique tips for optimal outcomes. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2018; 14: 353–5. - PubMed
-
- Yeung CK, Sihoe JD, Borzi PA. Endoscopic cross‐trigonal ureteral reimplantation under carbon dioxide bladder insufflation: a novel technique. J. Endourol. 2005; 19: 295–9. - PubMed
-
- Michaud JE, Akhavan A. Upper pole heminephrectomy versus lower pole ureteroureterostomy for ectopic upper pole ureters. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2017; 18: 21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
