A dynamic and collaborative approach to trial recruitment in safetxt, a UK sexual health randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35253453
- PMCID: PMC9203664
- DOI: 10.1177/17407745221078882
A dynamic and collaborative approach to trial recruitment in safetxt, a UK sexual health randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background/aims: Recruiting to target in randomised controlled trials is crucial for providing reliable results, yet many trials struggle to achieve their target sample size. Many trials do not report sufficient, if any, details of their recruitment strategy for others to adapt for their own trials. Furthermore, much of the available evidence describes strategies to improve recruitment aimed at participants, as opposed to strategies aimed at engaging and motivating recruiting staff who are deemed essential for recruitment success. The safetxt trial aimed to recruit 6250 participants, aged 16-24 years, who had either tested positive, or received treatment, for chlamydia/gonorrhoea/non-specific urethritis in the last 2 weeks, from across the United Kingdom into a randomised controlled trial investigating a text message intervention to improve sexual health outcomes. In this article, we describe in detail the recruitment strategies we employed that were primarily aimed at recruiters.
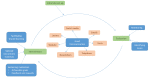
Methods: Recruitment began in April 2016. We built on our recruitment methods established in the pilot trial and developed several strategies to increase recruitment as the trial progressed including optimising site set-up, monitoring recruitment progress and identifying issues, facilitating shared learning, tailored recruitment materials, sustaining motivation, and communication. We describe these strategies in detail and provide practical examples for each.
Results: We combine our strategies for increasing recruitment into one cyclical approach whereby progress is continuously monitored, and interventions to improve recruitment are implemented. The site initiation visits were used to develop a clear recruitment plan and establish good relationships with local site staff. Screening logs were particularly helpful for monitoring recruitment challenges. We facilitated shared learning by organising meetings with recruiting sites and conducting site visits. Tailored recruitment materials helped to promote the trial in clinic environments, and rewards and goals helped sustain motivation among recruiting staff. Finally, at the centre of the approach is good communication which ensured we maintained good relationships with local site staff.
Conclusion: We conducted a large, multi-centre trial and successfully recruited to target. Our dynamic collaborative approach to recruitment described in this paper builds upon previous research by combining suggested good practice into one cyclical approach to recruitment, and providing detailed examples of each strategy. It is not possible to attribute a causal link between our approach and recruitment success overall, or with specific sites or recruiting staff. Nonetheless we describe the processes we used to build a good relationship with recruiting staff and sites, and maintain recruitment of large numbers of participants over the 32 months of the trial. Other researchers can use our approach and adapt our examples for their own trials.
Keywords: Recruitment; approach; intervention; randomised controlled trial; recruiter; recruiting staff; sexual health; strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous