Heat Shock-Binding Protein 21 Regulates the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection
- PMID: 35254105
- PMCID: PMC9006932
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00001-22
Heat Shock-Binding Protein 21 Regulates the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection
Abstract
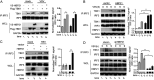
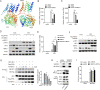
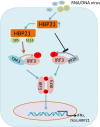
The induction of interferons (IFNs) plays an important role in the elimination of invading pathogens. Heat shock binding protein 21 (HBP21), first known as a molecular chaperone of HSP70, is involved in tumor development. Heat shock binding proteins have been shown to regulate diverse biological processes, such as cell cycle, kinetochore localization, transcription, and cilium formation. Their role in antimicrobial immunity remains unknown. Here, we found that HBP21 drives a positive feedback loop to promote IRF3-mediated IFN production triggered by viral infection. HBP21 deficiency significantly impaired the virus-induced production of IFN and resulted in greater susceptibility to viral infection both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, HBP21 interacted with IRF3 and promoted the formation of a TBK1-IRF3 complex. Moreover, HBP21 abolished the interaction between PP2A and IRF3 to repress the dephosphorylation of IRF3. Analysis of HBP21 protein structure further confirmed that HBP21 promotes the activation of IRF3 by depressing the dephosphorylation of IRF3 by PP2A. Further study demonstrated that virus-induced phosphorylation of Ser85 and Ser153 of HBP21 itself is important for the phosphorylation and dimerization of IRF3. Our study identifies HBP21 as a new positive regulator of innate antiviral response, which adds novel insight into activation of IRF3 controlled by multiple networks that specify behavior of tumors and immunity. IMPORTANCE The innate immune system is the first-line host defense against microbial pathogen invasion. The physiological functions of molecular chaperones, involving cell differentiation, migration, proliferation and inflammation, have been intensively studied. HBP21 as a molecular chaperone is critical for tumor development. Tumor is related to immunity. Whether HBP21 regulates immunity remains unknown. Here, we found that HBP21 promotes innate immunity response by dual regulation of IRF3. HBP21 interacts with IRF3 and promotes the formation of a TBK1-IRF3 complex. Moreover, HBP21 disturbs the interaction between PP2A and IRF3 to depress the dephosphorylation of IRF3. Analysis of HBP21 protein structure confirms that HBP21 promotes the activation of IRF3 by blocking the dephosphorylation of IRF3 by PP2A. Interestingly, virus-induced Ser85 and Ser153 phosphorylation of HBP21 is important for IRF3 activation. Our findings add to the known novel immunological functions of molecular chaperones and provide new insights into the regulation of innate immunity.
Keywords: HSP70; IRF3; PP2A; heat shock-binding protein 21; innate immunity; interferons; molecular chaperone; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Role of Long Noncoding RNA BST2-2 in the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection.J Virol. 2022 Apr 13;96(7):e0020722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00207-22. Epub 2022 Mar 17. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35297670 Free PMC article.
-
IRF1 Promotes the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection by Enhancing the Activation of IRF3.J Virol. 2020 Oct 27;94(22):e01231-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01231-20. Print 2020 Oct 27. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32878885 Free PMC article.
-
eIF4A3 Promotes RNA Viruses' Replication by Inhibiting Innate Immune Responses.J Virol. 2022 Nov 23;96(22):e0151322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01513-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36314820 Free PMC article.
-
TANK-binding kinase 1 as a novel therapeutic target for viral diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 May;23(5):437-446. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1601702. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30932713 Review.
-
Regulation of IRF3 activation in human antiviral signaling pathways.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;200:115026. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115026. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35367198 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening for Lipid-Metabolism-Related Genes and Identifying the Diagnostic Potential of ANGPTL6 for HBV-Related Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 17;12(11):1700. doi: 10.3390/biom12111700. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421714 Free PMC article.
-
REGγ regulates antiviral response by activating TBK1-IFNβ signaling through degradation of PPP2CB.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jul 30;82(1):296. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05816-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40736577 Free PMC article.
-
HBP21 Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Targeting PI3K/AKT-Mediated M1 Macrophage Polarization.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Jul 27;2025:9021628. doi: 10.1155/mi/9021628. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40757051 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein HSPA13 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by stabilizing TANK.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 8;9(1):443. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01735-0. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38062023 Free PMC article.
-
The dual functions of KDM7A in HBV replication and immune microenvironment.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 25;11(5):e0164123. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01641-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37623314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King KR, Aguirre AD, Ye YX, Sun Y, Roh JD, Ng RP, Jr, Kohler RH, Arlauckas SP, Iwamoto Y, Savol A, Sadreyev RI, Kelly M, Fitzgibbons TP, Fitzgerald KA, Mitchison T, Libby P, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R. 2017. IRF3 and type I interferons fuel a fatal response to myocardial infarction. Nat Med 23:1481–1487. 10.1038/nm.4428. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

