Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19
- PMID: 35255492
- PMCID: PMC9259496
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04576-6
Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19
Abstract
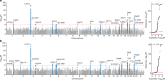
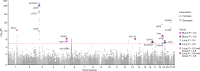
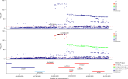
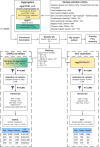
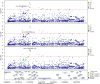
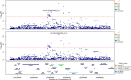
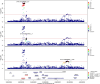
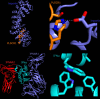
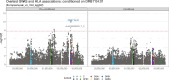
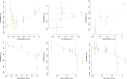
Critical COVID-19 is caused by immune-mediated inflammatory lung injury. Host genetic variation influences the development of illness requiring critical care1 or hospitalization2-4 after infection with SARS-CoV-2. The GenOMICC (Genetics of Mortality in Critical Care) study enables the comparison of genomes from individuals who are critically ill with those of population controls to find underlying disease mechanisms. Here we use whole-genome sequencing in 7,491 critically ill individuals compared with 48,400 controls to discover and replicate 23 independent variants that significantly predispose to critical COVID-19. We identify 16 new independent associations, including variants within genes that are involved in interferon signalling (IL10RB and PLSCR1), leucocyte differentiation (BCL11A) and blood-type antigen secretor status (FUT2). Using transcriptome-wide association and colocalization to infer the effect of gene expression on disease severity, we find evidence that implicates multiple genes-including reduced expression of a membrane flippase (ATP11A), and increased expression of a mucin (MUC1)-in critical disease. Mendelian randomization provides evidence in support of causal roles for myeloid cell adhesion molecules (SELE, ICAM5 and CD209) and the coagulation factor F8, all of which are potentially druggable targets. Our results are broadly consistent with a multi-component model of COVID-19 pathophysiology, in which at least two distinct mechanisms can predispose to life-threatening disease: failure to control viral replication; or an enhanced tendency towards pulmonary inflammation and intravascular coagulation. We show that comparison between cases of critical illness and population controls is highly efficient for the detection of therapeutically relevant mechanisms of disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.A.K., J.E.H., A.B., G.R.A. and M.A.R.F. are current employees and/or stockholders of Regeneron Genetics Center or Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Genomics England is a wholly owned Department of Health and Social Care company created in 2013 to work with the NHS to introduce advanced genomic technologies and analytics into healthcare. All Genomics England affiliated authors are, or were, salaried by Genomics England during this programme. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests relating to this work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG009740/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_20004/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_20058/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_20029/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_19059/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RC2 AG036495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204979/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RC4 AG039029/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 210561/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12008/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 223164/Z/21/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/R026408/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_14089/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N02995X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_19025/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

