Drivers of non-zero physician global scores during periods of inactive disease in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- PMID: 35256534
- PMCID: PMC8905981
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002042
Drivers of non-zero physician global scores during periods of inactive disease in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the frequency in which the physician provides a global assessment of disease activity (PhGA) >0 and an active joint count (AJC)=0 in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and search for determinants of divergence between the two measures.
Methods: Data were extracted from a multinational cross-sectional dataset of 9966 patients who had JIA by International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria, were recruited between 2011 and 2016, and had both PhGA and AJC recorded by the caring paediatric rheumatologist at the study visit. Determinants of discordance between PhGA>0 and AJC=0 were searched for by multivariable logistic regression and dominance analyses.
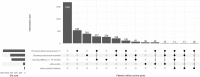
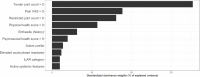
Results: The PhGA was scored >0 in 1647 (32.3%) of 5103 patients who had an AJC of 0. Independent associations with discordant assessment were identified for tender or restricted joint count >0, history of enthesitis, presence of active uveitis or systemic features, enthesitis-related or systemic arthritis, increased acute phase reactants, pain visual analogue scale (VAS)>0, and impaired physical or psychosocial well-being. In dominance analysis, tender joint count accounted for 35.43% of PhGA variance, followed by pain VAS>0 (17.72%), restricted joint count >0 (16.14%) and physical health score >0 (11.42%).
Conclusion: We found that many paediatric rheumatologists did not mark a score of 0 for patients who they found not to have active joints. The presence of pain in joints not meeting the definition of active joint used in JIA was the main determinant of this phenomenon.
Keywords: arthritis; arthritis, juvenile; outcome assessment, health care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Ruperto N, Ravelli A, Falcini F. Responsiveness of outcome measures in juvenile chronic arthritis. Rheumatology 1999;38:176–80. - PubMed
