Behavioral phenotyping of a rat model of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism reveals selective impairment of fear memory
- PMID: 35256586
- PMCID: PMC8901920
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-01858-5
Behavioral phenotyping of a rat model of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism reveals selective impairment of fear memory
Abstract
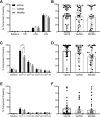
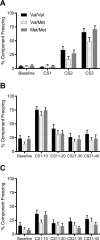
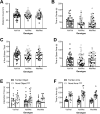
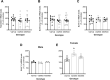
The common brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism is associated with reduced activity-dependent BDNF release and increased risk for anxiety disorders and PTSD. Here we behaviorally phenotyped a novel Val66Met rat model with an equivalent valine to methionine substitution in the rat Bdnf gene (Val68Met). In a three-day fear conditioning protocol of fear learning and extinction, adult rats with the Met/Met genotype demonstrated impaired fear memory compared to Val/Met rats and Val/Val controls, with no genotype differences in fear learning or extinction. This deficit in fear memory occurred irrespective of the sex of the animals and was not seen in adolescence (4 weeks of age). There were no changes in open-field locomotor activity or anxiety measured in the elevated plus maze (EPM) nor in other types of memory measured using the novel-object recognition test or Y-maze. BDNF exon VI expression in the dorsal hippocampus was higher and BDNF protein level in the ventral hippocampus was lower in female Val/Met rats than female Val/Val rats, with no other genotype differences, including in total BDNF, BDNF long, or BDNF IV mRNA. These data suggest a specific role for the BDNF Met/Met genotype in fear memory in rats. Further studies are required to investigate gene-environment interactions in this novel animal model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired fear memory in a rat model of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism is reversed by chronic exercise.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2023 Sep;203:107779. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2023.107779. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2023. PMID: 37269900
-
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor VAL68MET polymorphism modulates how developmental ethanol exposure impacts the hippocampus.Genes Brain Behav. 2019 Mar;18(3):e12484. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12484. Epub 2018 May 28. Genes Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 29691979 Free PMC article.
-
The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism moderates the relationship between Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and fear extinction learning.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 May;91:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29550677
-
The impact of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism on cognition in Bipolar Disorder: A review: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD. This Section of JAD focuses on the relevance of translational and neuroscience studies in providing a better understanding of the neural basis of affective disorders. The main aim is to briefly summaries relevant research findings in clinical neuroscience with particular regards to specific innovative topics in mood and anxiety disorders.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:552-558. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.07.054. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30078664 Review.
-
Interaction of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor, Exercise, and Fear Extinction: Implications for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(4):543-556. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230724101321. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37491857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing exposure therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a randomized clinical trial of virtual reality and imaginal exposure with a cognitive enhancer.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):299. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02066-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35896533 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Rat Model of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met Polymorphism Shows Attenuated Motivation for Alcohol Self-Administration and Diminished Propensity for Cue-Induced Relapse in Females.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 31;12(6):799. doi: 10.3390/biology12060799. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372084 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exercise on Tramadol-Conditioned Place Preference.Brain Sci. 2025 Jan 18;15(1):89. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15010089. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 39851456 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic exercise improves executive functions in females, but not males, without the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Apr 3;14(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00499-7. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37013586 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Testing Prepulse Inhibition of Acoustic Startle in Rodents.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2746:121-133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3585-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38070085

