Arsenic Transformation in Soil-Rice System Affected by Iron-Oxidizing Strain (Ochrobactrum sp.) and Related Soil Metabolomics Analysis
- PMID: 35256871
- PMCID: PMC8897285
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.794950
Arsenic Transformation in Soil-Rice System Affected by Iron-Oxidizing Strain (Ochrobactrum sp.) and Related Soil Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
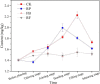
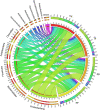
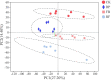
Iron-oxidizing bacteria (FeOB) could oxidize Fe(II) and mediate biomineralization, which provides the possibility for its potential application in arsenic (As) remediation. In the present study, a strain named Ochrobactrum EEELCW01 isolated previously, was inoculated into paddy soils to investigate the effect of FeOB inoculation on the As migration and transformation in paddy soils. The results showed that inoculation of Ochrobactrum sp. increased the proportion of As in iron-aluminum oxide binding fraction, which reduced the As bioavailability in paddy soils and effectively reduced the As accumulation in rice tissues. Moreover, the inoculation of iron oxidizing bacteria increased the abundance of KD4-96, Pedosphaeraceae and other bacteria in the soils, which could reduce the As toxicity in the soil through biotransformation. The abundance of metabolites such as carnosine, MG (0:0/14:0/0:0) and pantetheine 4'-phosphate increased in rhizosphere soils inoculated with FeOB, which indicated that the defense ability of soil-microorganism-plant system against peroxidation caused by As was enhanced. This study proved that FeOB have the potential application in remediation of As pollution in paddy soil, FeOB promotes the formation of iron oxide in paddy soil, and then adsorbed and coprecipitated with arsenic. On the other hand, the inoculation of Ochrobactrum sp. change soil microbial community structure and soil metabolism, increase the abundance of FeOB in soil, promote the biotransformation process of As in soil, and enhance the resistance of soil to peroxide pollution (As pollution).
Keywords: arsenic; iron-oxidizing bacteria; metabolomics; microbial community; paddy soil.
Copyright © 2022 Qian, Wu, Pan, Xiong, Xia and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Alam R., McPhedran K. (2019). Applications of biological sulfate reduction for remediation of arsenic. Chemosphere 222 932–944. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.194 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

