Long non-coding RNA screening and identification of potential biomarkers for type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 35257412
- PMCID: PMC8993646
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24280
Long non-coding RNA screening and identification of potential biomarkers for type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: To investigate new lncRNAs as molecular markers of T2D.
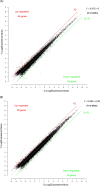
Methods: We used microarrays to identify differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs from five patients with T2D and paired controls. Through bioinformatics analysis, qRT-PCR validation, ELISA, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of 100 patients with T2D and 100 controls to evaluate the correlation between lncRNAs and T2D, and whether lncRNAs could be used in the diagnosis of T2D patients.
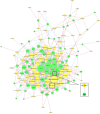
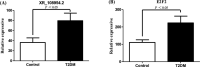
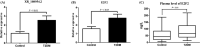
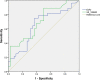
Results: We identified 68 and 74 differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs, respectively. The top five upregulated lncRNAs are ENST00000381108.3, ENST00000515544.1, ENST00000539543.1, ENST00000508174.1, and ENST00000564527.1, and the top five downregulated lncRNAs are TCONS_00017539, ENST00000430816.1, ENST00000533203.1, ENST00000609522.1, and ENST00000417079.1. The top five upregulated mRNAs are Q59H50, CYP27A1, DNASE1L3, GRIP2, and lnc-TMEM18-12, and the top five downregulated mRNAs are GSTM4, PODN, GLYATL2, ZNF772, and CLTC. Examination of lncRNA-mRNA interaction pairs indicated that the target gene of lncRNA XR_108954.2 is E2F2. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that XR_108954.2 (r = 0.387, p < 0.01) and E2F2 (r = 0.368, p < 0.01) expression levels were positively correlated with glucose metabolism indicators. Moreover, E2F2 was positively correlated with lipid metabolism indicators (r = 0.333, p < 0.05). The area under the ROC curve was 0.704 (95% CI: 0.578-0.830, p = 0.05) for lncRNA XR_108954.2 and 0.653 (95% CI: 0.516-0.790, p = 0.035) for E2F2.
Conclusions: This transcriptome analysis explored the aberrantly expressed lncRNAs and identified E2F2 and lncRNA XR_108954.2 as potential biomarkers for patients with T2D.
Keywords: biological markers; expression regulation; lncRNA; microarray analysis; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deregulation of lncRNA HIST1H2AG-6 and AIM1-3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Jun 6;14(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00994-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34092238 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lncRNA and GCKR gene in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Feb;501:66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31756311
-
Aberrant Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Indicates Potential Roles in Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2367-2378. doi: 10.1159/000484388. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29073614
-
Long noncoding RNA and messenger RNA abnormalities in pediatric sepsis: a preliminary study.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Mar 10;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-0698-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32151258 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
LncRNAs Landscape in the patients of primary gout by microarray analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 18;16(2):e0232918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232918. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33600466 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Screening of common genomic biomarkers to explore common drugs for the treatment of pancreatic and kidney cancers with type-2 diabetes through bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 2;15(1):7363. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91875-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40025145 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for diabetes mellitus and complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes. 2023 Dec 23;16(2):e13510. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13510. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 38140829 Free PMC article.
-
In silico identification and functional prediction of differentially expressed genes in South Asian populations associated with type 2 diabetes.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 14;18(12):e0294399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294399. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38096208 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Long Non-Coding RNA in Anxiety Disorders: A Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 23;26(11):5042. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115042. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chan M. China's burgeoning epidemic of diabetes‐associated mortality. JAMA. 2017;317(3):264‐266. - PubMed
-
- Krentz NAJ, Gloyn AL. Insights into pancreatic islet cell dysfunction from type 2 diabetes mellitus genetics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(4):202‐212. - PubMed
-
- Ng CS, Lee JYC, Toh MP, Ko Y. Cost‐of‐illness studies of diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;105(2):151‐163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82060589/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81960258/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81860179/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- SKL-HIDCA-2019-39/State Key Laboratory of Pathogenesis, Prevention and Treatment of High Incidence Diseases in Central Asia
- 2018D01C177/Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

