Pain and functional disability amongst adults with moderate and severe haemophilia from the Irish personalised approach to the treatment of haemophilia (iPATH) study
- PMID: 35258118
- PMCID: PMC9311204
- DOI: 10.1111/ejh.13763
Pain and functional disability amongst adults with moderate and severe haemophilia from the Irish personalised approach to the treatment of haemophilia (iPATH) study
Abstract
Objectives: To establish the prevalence of pain and functional disability in Irish adults with moderate and severe haemophilia, and to examine demographic and lifestyle influences.
Methods: Males ≥18 years with moderate or severe haemophilia participated. Pain and function were examined using the PROBE questionnaire.
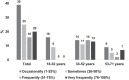
Results: Of 49 participants [median age 44 (IQR 32, 52) years], most had severe haemophilia (Factor VIII = 30; Factor IX = 13) and were on regular prophylaxis (88%). Those with moderate haemophilia (Factor VIII = 5; Factor IX = 1) treated on demand (12%). Acute (72%) and chronic pain (71%), functional difficulties (58%), and analgesic requirements (92%) were prevalent. Age was significantly associated with more advanced haemophilic arthropathy (p = .002), chronic pain (p = .029) and functional difficulties (p = .036). Adults who reported chronic pain commenced prophylaxis significantly later in life [32 (20, 51) vs. 8 (1, 23) years; p = .004]. Physical activity was significantly lower in those with functional difficulties (p < .05). A disparity between self-perceived 'target joints' and clinically defined target joints was also identified (76% vs. 23%).
Conclusion: Haemophilic arthropathy, pain and functional disability were prevalent amongst Irish adults with moderate and severe haemophilia. Age-dependent lifestyle, analgesic and treatment influences on pain and function warrant further investigation.
Keywords: function; haemophilia; pain; physical activity; prophylaxis.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
M.L. has served on an advisory board to Tremeau Pharmaceuticals and as a consultant to Sobi. She received indirect funding from Takeda for the development of educational material. N.M. O’C. has received research support from SOBI; participated in advisory boards for F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd, UniQure, SOBI, Freeline; and participated in speakers’ bureaus for F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd, SOBI and Novo Nordisk. J.S. O’D. has served on the speaker's bureau for Baxter, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Leo Pharma, Takeda and Octapharma. He has also served on the advisory boards of Baxter, Bayer, Octapharma CSL Behring, Daiichi Sankyo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda and Pfizer. J.S. O’D. has received research grant funding awards from Baxter, Bayer, Pfizer, Shire (now part of Takeda), Takeda and Novo Nordisk. P.L.T. is full‐time employee of Baxalta Innovations GmbH, a member of the Takeda group of companies, and shareholder of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. M.K. has served on an advisory council to Takeda. The remaining authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mannucci PM, Tuddenham EG. The hemophilias–from royal genes to gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(23):1773‐1779. - PubMed
-
- Raffini L, Manno C. Modern management of haemophilic arthropathy. Br J Haematol. 2007;136(6):777‐787. - PubMed
-
- Franchini M, Mannucci PM. Modifiers of clinical phenotype in severe congenital hemophilia. Thromb Res. 2017;156:60‐64. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, et al. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia. 2020;26(S6):1‐158. - PubMed
-
- Mancuso ME, Mahlangu JN, Pipe SW. The changing treatment landscape in haemophilia: from standard half‐life clotting factor concentrates to gene editing. Lancet. 2021;397(10274):630‐640. - PubMed