Inhibition of the ISR abrogates mGluR5-dependent long-term depression and spatial memory deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35260557
- PMCID: PMC8904583
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-01862-9
Inhibition of the ISR abrogates mGluR5-dependent long-term depression and spatial memory deficits in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
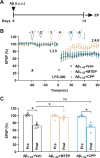
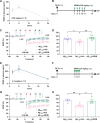
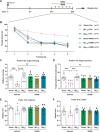
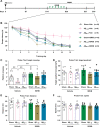
Soluble amyloid-β-protein (Aβ) oligomers, a major hallmark of AD, trigger the integrated stress response (ISR) via multiple pathologies including neuronal hyperactivation, microvascular hypoxia, and neuroinflammation. Increasing eIF2α phosphorylation, the core event of ISR, facilitates metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR)-dependent long-term depression (LTD), and suppressing its phosphorylation has the opposite effect. Having found the facilitation of mGluR5-LTD by Aβ in live rats, we wondered if suppressing eIF2α phosphorylation cascade would protect against the synaptic plasticity and cognitive disrupting effects of Aβ. We demonstrate here that the facilitation of mGluR5-LTD in a delayed rat model by single i.c.v. injection of synthetic Aβ1-42. Systemic administration of the small-molecule inhibitor of the ISR called ISRIB (trans-isomer) prevents Aβ-facilitated LTD and abrogates spatial learning and memory deficits in the hippocampus in exogenous synthetic Aβ-injected rats. Moreover, ex vivo evidence indicates that ISRIB normalizes protein synthesis in the hippocampus. Targeting the ISR by suppressing the eIF2α phosphorylation cascade with the eIF2B activator ISRIB may provide protective effects against the synaptic and cognitive disruptive effects of Aβ which likely mediate the early stage of sporadic AD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repression of the eIF2α kinase PERK alleviates mGluR-LTD impairments in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2016 May;41:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Neurobiol Aging. 2016. PMID: 27103515 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of long-term depression by soluble amyloid β protein in rat hippocampus is mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptor and involves activation of p38MAPK, STEP and caspase-3.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 3;253:435-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.054. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24012839
-
REDD1 Is Involved in Amyloid β-Induced Synaptic Dysfunction and Memory Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 13;21(24):9482. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249482. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322202 Free PMC article.
-
Notoginseng Saponin Rg1 Prevents Cognitive Impairment through Modulating APP Processing in Aβ1-42-injected Rats.Curr Med Sci. 2019 Apr;39(2):196-203. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2019-1. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Curr Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31016510
-
Noncanonical Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jan 6;62:235-254. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-021821-091747. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34516293 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the Integrated Stress Response Prevents Natural Forgetting and Corrects Accelerated Forgetting Associated with Epilepsy.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May;62(5):6059-6069. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04669-5. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39708234
-
Zunyimycin C enhances immunity and improves cognitive impairment and its mechanism.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 12;12:1081243. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1081243. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36579344 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive human Alzheimer brain soluble Aβ: pathophysiology and therapeutic opportunities.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;27(8):3182-3191. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01589-5. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35484241 Review.
-
On the Inadequacy of the Current Transgenic Animal Models of Alzheimer's Disease: The Path Forward.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2981. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052981. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474228 Free PMC article.
-
The integrated stress response in neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Feb 19;20(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00811-6. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 39972469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roussel BD, Kruppa AJ, Miranda E, Crowther DC, Lomas DA, Marciniak SJ. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:105–18. - PubMed
-
- Moon SL, Sonenberg N, Parker R. Neuronal regulation of eIF2alpha function in health and neurological disorders. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24:575–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

