Automated detection of celiac disease using Machine Learning Algorithms
- PMID: 35260574
- PMCID: PMC8904634
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-07199-z
Automated detection of celiac disease using Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
Celiac disease is a disorder of the immune system that mainly affects the small intestine but can also affect the skeletal system. The diagnosis relies on histological assessment of duodenal biopsies acquired by upper digestive endoscopy. Immunological tests involve collecting a blood sample to detect if the antibodies have been produced in the body. Endoscopy is invasive and histology is time-consuming. In recent years there have been various algorithms that use artificial intelligence (AI) and neural convolutions (CNN, Convolutional Neural Network) to process images from capsule endoscopy, a non-invasive endoscopy approach, that provides magnified, high qualitative images of the small bowel mucosa, to quickly establish a diagnosis. The proposed innovative approach do not use complex learning algorithms, instead it find some artefacts in the endoscopies using kernels and use classified machine learning algorithms. Each used artefacts have a psychical meaning: atrophies of the mucosa with a visible submucosal vascular pattern; the presence of cracks (depressions) that have an appearance similar to that of dry land; reduction or complete loss of folds in the duodenum; the presence of a submerged appearance at the Kerckring folds and a low number of villi. The results obtained for video capsule endoscopy images processing reveal an accuracy of 94.1% and F1 score of 94%, which is competitive with other complex algorithms. The main goal of the present research was to demonstrate that computer-aided diagnosis of celiac disease is possible even without the use of very complex algorithms, which require expensive hardware and a lot of processing time. The use of the proposed automated images processing acquired noninvasively by capsule endoscopy would be assistive in detecting the subtle presence of villous atrophy not evident by visual inspection. It may also be useful to assess the degree of improvement of celiac. Patients on a gluten-free diet, the main treatment method for stopping the autoimmune process and improving the state of the small intestinal villi. The novelty of the work is that the algorithm uses two modified filters to properly analyse the intestine wall texture. It is proved that using the right filters, the proper diagnostic can be obtained by image processing, without the use of a complicated machine learning algorithm.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




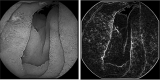
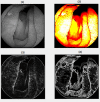
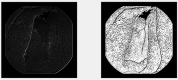
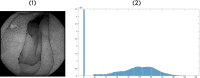










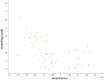
Similar articles
-
The role of capsule endoscopy in suspected celiac disease patients with positive celiac serology.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Feb;56(2):499-505. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1290-6. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20552401
-
Methods to quantitate videocapsule endoscopy images in celiac disease.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(6):1895-911. doi: 10.3233/BME-140999. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014. PMID: 25226886 Review.
-
Celiac disease diagnosis from videocapsule endoscopy images with residual learning and deep feature extraction.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Apr;187:105236. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105236. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 31786452
-
Capsule Endoscopy and Enteroscopy in Celiac Disease.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2019 Mar;48(1):73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30711212 Review.
-
Extraction and processing of videocapsule data to detect and measure the presence of villous atrophy in celiac disease patients.Comput Biol Med. 2016 Nov 1;78:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Comput Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27673492
Cited by
-
QRNet: A Quaternion-Based Retinex Framework for Enhanced Wireless Capsule Endoscopy Image Quality.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;12(3):239. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030239. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150703 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;9(8):493. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9080493. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning Multi-Domain Model Provides Accurate Detection and Grading of Mucosal Ulcers in Different Capsule Endoscopy Types.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;12(10):2490. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102490. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292178 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Assisted Algorithm for Quantification of Fibrosis by Native Cardiac CT: A Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 15;13(16):4807. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164807. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200950 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular basis of proximal small intestine disorders.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;21(10):687-709. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00962-9. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39117867 Review.
References
-
- Popp A, Balaba VD, Mäki M. Celiac disease. In: Gershman G, Thomson M, editors. Practical Pediatric Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Wiley; 2021. pp. 207–211.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

