Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35261183
- PMCID: PMC9178168
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12976
Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D supplementation is proposed as a potentially effective nutritional intervention to mitigate the risk of sarcopenia. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to investigate the impact of vitamin D supplementation monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults.
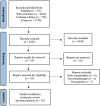
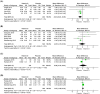
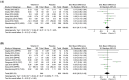
Methods: A comprehensive search of the literature was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. Eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) compared the effect of vitamin D supplementation (as monotherapy) with placebo on indices of sarcopenia in older (>50 years) adults. Using the random effects inverse-variance model, we calculated the mean difference (MD) in handgrip strength (HGS), short physical performance battery (SPPB), timed up and go (TUG), and appendicular lean mass (ALM) between groups. We also calculated the standardized mean difference (SMD) in general muscle strength and general physical performance (composite plot of all muscle strength and physical performance outcomes, respectively) between groups.
Results: Ten RCTs were included in the meta-analysis. A significant decrease in SPPB scores was observed with vitamin D supplementation compared with placebo (MD: -0.23; 95% CI -0.40 to -0.06; I2 = 0%; P = 0.007). Vitamin D supplementation conferred no effect on HGS (MD: -0.07 kg; 95% CI -0.70 to 0.55; I2 = 51%, P = 0.82), TUG (MD: 0.07 s; 95% CI -0.08 to 0.22; I2 = 0%, P = 0.35), ALM (MD: 0.06 kg/m2 ; 95% CI: -0.32 to 0.44; I2 = 73%, P = 0.77), general muscle strength (SMD: -0.01; 95% CI -0.17 to 0.15; I2 = 42%, P = 0.90), or general physical performance (SMD: -0.02; 95% CI -0.23 to 0.18; I2 = 71%, P = 0.83).
Conclusions: Vitamin D supplementation did not improve any sarcopenia indices in community-dwelling older adults and may compromise some aspects of physical performance. Future studies are warranted to investigate the impact of vitamin D supplementation on individual indices of SPPB, including mobility and balance, in older adults.
Keywords: Frailty; Handgrip strength; Older adults; Physical performance; Sarcopenia; Vitamin D.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on: "Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis" by Prokopidis et al.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Oct;13(5):2581-2583. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13038. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 35808899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The authors' reply: 'Comment on: "Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis" by Prokopidis et al.'.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Dec;13(6):2757-2758. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13087. Epub 2022 Sep 9. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 36082492 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Candow DG, Vogt E, Johannsmeyer S, Forbes SC, Farthing JP. Strategic creatine supplementation and resistance training in healthy older adults. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2015;40:689–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

