Intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy: shifting from sustained release to enhancing penetration into cartilage
- PMID: 35261301
- PMCID: PMC8920370
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2048130
Intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy: shifting from sustained release to enhancing penetration into cartilage
Abstract
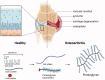
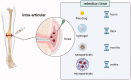
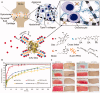
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive chronic inflammation that leads to cartilage degeneration. OA Patients are commonly given pharmacological treatment, but the available treatments are not sufficiently effective. The development of sustained-release drug delivery systems (DDSs) for OA may be an attractive strategy to prevent rapid drug clearance and improve the half-life of a drug at the joint cavity. Such delivery systems will improve the therapeutic effects of anti-inflammatory effects in the joint cavity. Whereas, for disease-modifying OA drugs (DMOADs) which target chondrocytes or act on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), the cartilage-permeable DDSs are required to maximize their efficacy. This review provides an overview of joint structure in healthy and pathological conditions, introduces the advances of the sustained-release DDSs and the permeable DDSs, and discusses the rational design of the permeable DDSs for OA treatment. We hope that the ideas generated in this review will promote the development of effective OA drugs in the future.
Keywords: Drug delivery system; intra-articular; osteoarthritis; permeability; sustained-release.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

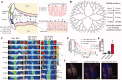
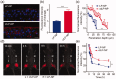
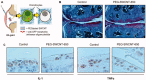
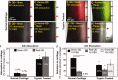
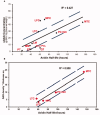

References
-
- Andres-Guerrero V, Zong M, Ramsay E, et al. (2015). Novel biodegradable polyesteramide microspheres for controlled drug delivery in Ophthalmology. J Control Release 211:105–17. - PubMed
-
- Ansboro S, Hayes JS, Barron V, et al. (2014). A chondromimetic microsphere for in situ spatially controlled chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Control Release 179:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Aydin O, Korkusuz F, Korkusuz P, et al. (2015). In vitro and in vivo evaluation of doxycycline-chondroitin sulfate/PCLmicrospheres for intraarticular treatment of osteoarthritis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 103:1238–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
