Esthesioneuroblastoma presenting with orbital signs and ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone syndrome
- PMID: 35261468
- PMCID: PMC8865228
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2021.2001260
Esthesioneuroblastoma presenting with orbital signs and ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone syndrome
Abstract
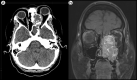
A 23-year-old woman with known nasal polyps and a recent seizure presented with diplopia, proptosis, extraocular motility deficits, and stigmata of Cushing syndrome. Computed tomography showed a left sinonasal mass extending into the left orbit. Laboratory evaluation revealed refractory hypokalemia and significantly elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone. Histopathologic exam confirmed the diagnosis of esthesioneuroblastoma.
Keywords: Esthesioneuroblastoma; neuroesthesioma; olfactory neuroblastoma; sinonasal tumor.
Copyright © 2021 Baylor University Medical Center.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
