Overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor protects chronic myeloid leukemia cells from apoptosis induced by etoposide
- PMID: 35261636
- PMCID: PMC8867183
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13242
Overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor protects chronic myeloid leukemia cells from apoptosis induced by etoposide
Abstract
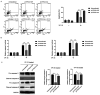
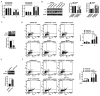
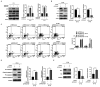
Resistance to apoptosis induced by chemotherapy is still an obstacle for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Numerous studies have indicated that upregulation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) protein expression reduced apoptosis induced by various factors. However, whether HGF has any effect on apoptosis induced by VP-16 (etoposide) in CML cells and its underlying mechanisms are unclear. HGF was overexpressed in the K562 cell line using transfection. The protein and mRNA expression levels, and the concentration of HGF were measured using western blot analysis, reverse transcription-quantitative (RT-qPCR) and ELISA respectively. Apoptosis in the K562 cell line was determined using flow cytometry and western blot analysis. Changes in cell viability were measured using a MTT assay. RT-qPCR and western blot analysis revealed that HGF was successfully upregulated at both the mRNA and protein expression levels in the K562 cell line, respectively. After VP-16 treatment, the number of apoptotic cells overexpressing HGF was lower compared with that in cells transfected with the empty vector. Mechanistic investigation revealed that overexpression of HGF led to the increase in Bcl-2 protein expression level and inhibition of caspase-3/9 activation. Furthermore, HGF overexpression resulted in activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Therefore, the results of the present study revealed that targeting HGF could be used as a strategy to overcome VP-16 resistance in CML.
Keywords: CML; HGF; VP-16; apoptosis.
Copyright © 2022, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
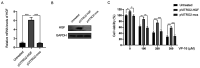
Similar articles
-
The Critical Role of PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Shikonin-Induced Apoptosis and Proliferation Inhibition of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(3):981-993. doi: 10.1159/000490142. Epub 2018 May 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29843123
-
[The effect of retrovirus-mediated HO-1 gene on chronic myeloid leukemia resistance cell K562/A02 apoptosis induced by nilotinib].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012 May;33(5):383-7. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781797 Chinese.
-
[Regulation of wild type PTEN gene on Survivin, Xiap and Smac in chronic leukemia cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Nov 1;91(40):2868-72. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22333553 Chinese.
-
Differential induction of etoposide-mediated apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 and K562 cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;46(4):605-11. Mol Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7969039
-
[Experimental study of up-regulating PTEN gene on increasing the chemosensitivity in K562/ADM cells].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012 May;33(5):412-6. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781804 Chinese.
Cited by
-
RTN2, a new member of circadian clock genes identified by database mining and bioinformatics prediction, is highly expressed in ovarian cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Nov;26(5):350. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12866. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 36177918 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
