Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities
- PMID: 35261644
- PMCID: PMC8888139
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2021.05.006
Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities
Abstract
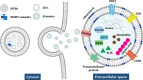
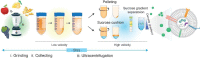
Nanotechnologies have been successfully applied to the treatment of various diseases. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PENs) are expected to become effective therapeutic modalities for treating disease or in drug-delivery. PENs are minimally cytotoxic to healthy tissues, with which they show excellent biocompatibility, and are biased towards tumors by targeting specific tissues through special endocytosis mechanisms. Thus, the use of these PENs may expand the scope of drug therapies while reducing the off-target effects. In this review, we summarize the fundamental features and bioactivities of PENs extracted from the grape, grapefruit, ginger, lemon, and broccoli and discuss the applications of these particles as therapeutics and nanocarriers.
Keywords: Drug-delivery systems; Exosomes; Nanocarriers; Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

