Polymeric microneedle-mediated sustained release systems: Design strategies and promising applications for drug delivery
- PMID: 35261645
- PMCID: PMC8888142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2021.07.002
Polymeric microneedle-mediated sustained release systems: Design strategies and promising applications for drug delivery
Abstract
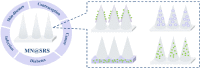
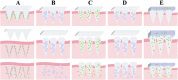
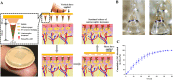
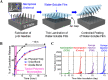
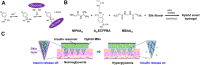
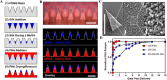
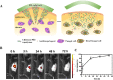
Parenteral sustained release drug formulations, acting as preferable platforms for long-term exposure therapy, have been wildly used in clinical practice. However, most of these delivery systems must be given by hypodermic injection. Therefore, issues including needle-phobic, needle-stick injuries and inappropriate reuse of needles would hamper the further applications of these delivery platforms. Microneedles (MNs) as a potential alternative system for hypodermic needles can benefit from minimally invasive and self-administration. Recently, polymeric microneedle-mediated sustained release systems (MN@SRS) have opened up a new way for treatment of many diseases. Here, we reviewed the recent researches in MN@SRS for transdermal delivery, and summed up its typical design strategies and applications in various diseases therapy, particularly focusing on the applications in contraception, infection, cancer, diabetes, and subcutaneous disease. An overview of the present clinical translation difficulties and future outlook of MN@SRS was also provided.
Keywords: Long-term exposure therapy; Microneedles; Sustained release; Transdermal drug delivery.
© 2021 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recent progress of polymeric microneedle-assisted long-acting transdermal drug delivery.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2024 Mar 20;27:12434. doi: 10.3389/jpps.2024.12434. eCollection 2024. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38571937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles-encapsulated polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery.J Control Release. 2020 Sep 10;325:163-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.039. Epub 2020 Jul 3. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32629134 Review.
-
Biodegradable polymeric insulin microneedles - a design and materials perspective review.Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2296350. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2296350. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38147499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-acting microneedle formulations.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023 Oct;201:115055. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115055. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023. PMID: 37597586 Review.
-
Microneedle array systems for long-acting drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Feb;159:44-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.12.006. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33359666 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapidly separating dissolving microneedles with sustained-release colchicine and stabilized uricase for simplified long-term gout management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Aug;13(8):3454-3470. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.011. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37655319 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis and visualization of transdermal drug delivery research in the last decade: global research trends and hotspots.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 16;14:1173251. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1173251. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37397493 Free PMC article.
-
Dissolvable polymeric microneedles loaded with aspirin for antiplatelet aggregation.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Jan;18(1):100776. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100776. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 36818956 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Polymer Microneedles Loaded with Interferon Alpha 1b for Treatment of Hyperplastic Scar.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;15(12):2621. doi: 10.3390/polym15122621. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376266 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin microcrystals deposited on high-density microneedle tips for the preparation of soluble polymer microneedles.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Oct;13(10):2639-2652. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01343-6. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37040032
References
-
- Chen Z., He J., Qi J., Zhu Q., Wu W., Lu Y. Long-acting microneedles: a progress report of the state-of-the-art techniques. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(8):1462–1468. - PubMed
-
- Chen M., Quan G., Sun Y., Yang D., Pan X., Wu C. Nanoparticles-encapsulated polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J Control Release. 2020;325:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Singh P., Carrier A., Chen Y., Lin S., Wang J., Cui S. Polymeric microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery. J Control Release. 2019;315:97–113. - PubMed
-
- Yarmush M.L., Golberg A., Sersa G., Kotnik T., Miklavcic D. Electroporation-based technologies for medicine: principles, applications, and challenges. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2014;16:295–320. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

