Advances in Nanoparticles for Effective Delivery of RNA Therapeutics
- PMID: 35261724
- PMCID: PMC8891745
- DOI: 10.1007/s13206-022-00052-5
Advances in Nanoparticles for Effective Delivery of RNA Therapeutics
Abstract
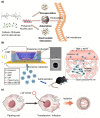
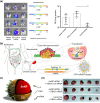
RNA therapeutics, including messenger RNA (mRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA), are genetic materials that mediate the translation of genetic direction from genes to induce or inhibit specific protein production. Although the interest in RNA therapeutics is rising globally, the absence of an effective delivery system is an obstacle to the clinical application of RNA therapeutics. Additionally, immunogenicity, short duration of protein expression, unwanted enzymatic degradation, and insufficient cellular uptake could limit the therapeutic efficacy of RNA therapeutics. In this regard, novel platforms based on nanoparticles are crucial for delivering RNAs to the targeted site to increase efficiency without toxicity. In this review, the most recent status of nanoparticles as RNA delivery vectors, with a focus on polymeric nanoparticles, peptide-derived nanoparticles, inorganic nanoparticles, and hybrid nanoparticles, is discussed. These nanoparticular platforms can be utilized for safe and effective RNA delivery to augment therapeutic effects. Ultimately, RNA therapeutics encapsulated in nanoparticle-based carriers will be used to treat many diseases and save lives.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Gene therapy; Nanomedicine; Nanoparticles; RNA delivery.
© The Korean BioChip Society 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
