Capacity for consciousness under ketamine anaesthesia is selectively associated with activity in posteromedial cortex in rats
- PMID: 35261778
- PMCID: PMC8896332
- DOI: 10.1093/nc/niac004
Capacity for consciousness under ketamine anaesthesia is selectively associated with activity in posteromedial cortex in rats
Abstract
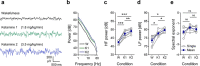
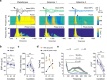
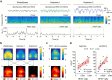
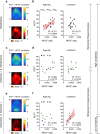
It remains unclear how specific cortical regions contribute to the brain's overall capacity for consciousness. Clarifying this could help distinguish between theories of consciousness. Here, we investigate the association between markers of regionally specific (de)activation and the brain's overall capacity for consciousness. We recorded electroencephalographic responses to cortical electrical stimulation in six rats and computed Perturbational Complexity Index state-transition (PCIST), which has been extensively validated as an index of the capacity for consciousness in humans. We also estimated the balance between activation and inhibition of specific cortical areas with the ratio between high and low frequency power from spontaneous electroencephalographic activity at each electrode. We repeated these measurements during wakefulness, and during two levels of ketamine anaesthesia: with the minimal dose needed to induce behavioural unresponsiveness and twice this dose. We found that PCIST was only slightly reduced from wakefulness to light ketamine anaesthesia, but dropped significantly with deeper anaesthesia. The high-dose effect was selectively associated with reduced high frequency/low frequency ratio in the posteromedial cortex, which strongly correlated with PCIST. Conversely, behavioural unresponsiveness induced by light ketamine anaesthesia was associated with similar spectral changes in frontal, but not posterior cortical regions. Thus, activity in the posteromedial cortex correlates with the capacity for consciousness, as assessed by PCIST, during different depths of ketamine anaesthesia, in rats, independently of behaviour. These results are discussed in relation to different theories of consciousness.
Keywords: EEG markers of consciousness; consciousness; ketamine anesthesia; perturbational complexity index.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased signal diversity/complexity of spontaneous EEG, but not evoked EEG responses, in ketamine-induced psychedelic state in humans.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 23;15(11):e0242056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242056. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33226992 Free PMC article.
-
Laminar evoked responses in mouse somatosensory cortex suggest a special role for deep layers in cortical complexity.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Mar;59(5):752-770. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16108. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37586411
-
The spectral exponent of the resting EEG indexes the presence of consciousness during unresponsiveness induced by propofol, xenon, and ketamine.Neuroimage. 2019 Apr 1;189:631-644. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.01.024. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30639334
-
Transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with high-density EEG in altered states of consciousness.Brain Inj. 2014;28(9):1180-9. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2014.920524. Brain Inj. 2014. PMID: 25099022 Review.
-
Cortical mechanisms of loss of consciousness: insight from TMS/EEG studies.Arch Ital Biol. 2012 Jun-Sep;150(2-3):44-55. doi: 10.4449/aib.v150i2.1361. Arch Ital Biol. 2012. PMID: 23165870 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of ketamine and thiopental anesthesia on ultraweak photon emission and oxidative-nitrosative stress in rat brains.Front Syst Neurosci. 2025 Mar 21;19:1502589. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2025.1502589. eCollection 2025. Front Syst Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40191280 Free PMC article.
-
Group ICA of wide-field calcium imaging data reveals the retrosplenial cortex as a major contributor to cortical activity during anesthesia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 May 10;18:1258793. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1258793. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38799987 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ketamine and propofol on muscarinic plateau potentials in rat neocortical pyramidal cells.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 2;20(1):e0316262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316262. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39746093 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring effects of anesthesia on complexity, differentiation, and integrated information in rat EEG.Neurosci Conscious. 2024 May 16;2024(1):niae021. doi: 10.1093/nc/niae021. eCollection 2024. Neurosci Conscious. 2024. PMID: 38757120 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic Mechanisms in Proteinoid-Based Protocells.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Feb 5;16(3):519-542. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00801. Epub 2025 Jan 22. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39840997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arena A, Thon S, Storm J. PCI-like measure in rodents. Hum Brain Project Neuroinf Platform 2019.doi: 10.25493/S0DM-BK5. - DOI
-
- Baars BJ. Global workspace theory of consciousness: toward a cognitive neuroscience of human experience. In: Laureys S (ed.), The Boundaries of Consciousness: Neurobiology and Neuropathology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005, 45–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
