An Updated Review of Subglottic Stenosis: Etiology, Evaluation, and Management
- PMID: 35261874
- PMCID: PMC8892813
- DOI: 10.1007/s13665-022-00286-6
An Updated Review of Subglottic Stenosis: Etiology, Evaluation, and Management
Abstract
Purpose of review: To assimilate the newly published literature regarding subglottic stenosis (SGS), including basic science and translational research on mechanisms of etiology, clinical diagnostics, and therapeutic treatments.
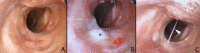
Recent findings: The role of inflammation in development of iatrogenic and idiopathic SGS (iSGS) is continuing to be studied. The IL-23/IL-17A inflammatory axis appears to be a potential mechanism for development of iSGS. Additionally, as anticipated in an inflammatory milieu, PD-1/PD-L1 expression is upregulated. If the PD-1/PD-L1 axis is important in SGS pathogenesis, then it may represent a potential target for immunotherapeutic inhibition, given its success in cancer treatment. In terms of surgical management, prospective studies show that endoscopic approaches have more frequent recurrence compared to open techniques.
Summary: SGS arises from various etiologies, and further understanding of its pathogenesis can aid in the development of novel therapies. It is imperative to obtain a thorough history for each patient presenting with respiratory complaints, as misdiagnosis can delay proper treatment. Endoscopic and open surgical techniques continue to be investigated in a growing number of prospective clinical trials to determine optimal treatment protocols. In-office injections are gaining popularity and show promise in the treatment of SGS.
Keywords: Iatrogenic; Idiopathic; Laryngotracheal stenosis; Review; Subglottic stenosis.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestNo disclosures relevant to the subject matter. Dr. Rosow reports a one-time payment from Springer for co-editing a published book.
Figures
References
-
- Rosow DE, Barbarite E. Review of adult laryngotracheal stenosis: pathogenesis, management, and outcomes. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;24:489–493. - PubMed
-
- Nouraei SAR, Ma E, Patel A, Howard DJ, Sandhu GS. Estimating the population incidence of adult post-intubation laryngotracheal stenosis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2007;32:411–412. - PubMed
-
- Poetker DM, Ettema SL, Blumin JH, Toohill RJ, Merati AL. Association of airway abnormalities and risk factors in 37 subglottic stenosis patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135:434–437. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
