This is a preprint.
Immunological memory to Common Cold Coronaviruses assessed longitudinally over a three-year period
- PMID: 35262082
- PMCID: PMC8902883
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.03.01.482548
Immunological memory to Common Cold Coronaviruses assessed longitudinally over a three-year period
Update in
-
Immunological memory to common cold coronaviruses assessed longitudinally over a three-year period pre-COVID19 pandemic.Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Sep 14;30(9):1269-1278.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.07.012. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Cell Host Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35932763 Free PMC article.
Abstract
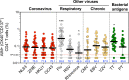
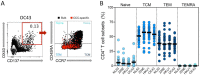
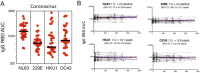
Understanding immune memory to Common Cold Coronaviruses (CCCs) is relevant for assessing its potential impact on the outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and for the prospects of pan-corona vaccines development. We performed a longitudinal analysis, of pre-pandemic samples collected from 2016-2019. CD4+ T cells and antibody responses specific for CCC and to other respiratory viruses, and chronic or ubiquitous pathogens were assessed. CCC-specific memory CD4+ T cells were detected in most subjects, and their frequencies were comparable to those for other common antigens. Notably, responses to CCC and other antigens such as influenza and Tetanus Toxoid (TT) were sustained over time. CCC-specific CD4+ T cell responses were also associated with low numbers of HLA-DR+CD38+ cells and their magnitude did not correlate with yearly changes in the prevalence of CCC infections. Similarly, spike RBD-specific IgG responses for CCC were stable throughout the sampling period. Finally, high CD4+ T cell reactivity to CCC, but not antibody responses, was associated with high pre-existing SARS-CoV-2 immunity. Overall, these results suggest that the steady and sustained CCC responses observed in the study cohort are likely due to a relatively stable pool of CCC-specific memory CD4+ T cells instead of fast decaying responses and frequent reinfections.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
A.Se. is a consultant for Gritstone Bio, Flow Pharma, Arcturus Therapeutics, ImmunoScape, CellCarta, Avalia, Moderna, Fortress and Repertoire. S.C. is a consultant for Avalia. LJI has filed for patent protection for various aspects of SARS-CoV-2 epitope pools design. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Materials & Correspondence
Epitope pools used in this study will be made available to the scientific community upon request, and following execution of a material transfer agreement (MTA), by contacting A.S. (
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
