Pum2 and TDP-43 refine area-specific cytoarchitecture post-mitotically and modulate translation of Sox5, Bcl11b, and Rorb mRNAs in developing mouse neocortex
- PMID: 35262486
- PMCID: PMC8906809
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55199
Pum2 and TDP-43 refine area-specific cytoarchitecture post-mitotically and modulate translation of Sox5, Bcl11b, and Rorb mRNAs in developing mouse neocortex
Abstract
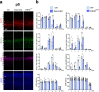
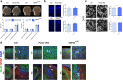
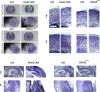
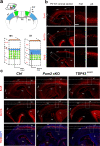
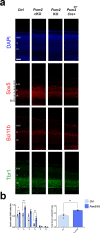
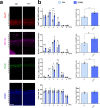
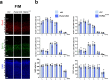
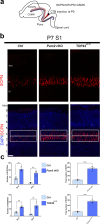
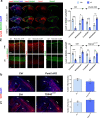
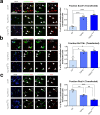
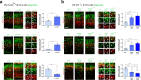
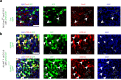
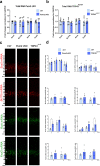
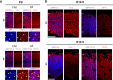
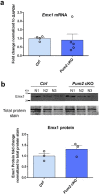
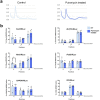
In the neocortex, functionally distinct areas process specific types of information. Area identity is established by morphogens and transcriptional master regulators, but downstream mechanisms driving area-specific neuronal specification remain unclear. Here, we reveal a role for RNA-binding proteins in defining area-specific cytoarchitecture. Mice lacking Pum2 or overexpressing human TDP-43 show apparent 'motorization' of layers IV and V of primary somatosensory cortex (S1), characterized by dramatic expansion of cells co-expressing Sox5 and Bcl11b/Ctip2, a hallmark of subcerebral projection neurons, at the expense of cells expressing the layer IV neuronal marker Rorβ. Moreover, retrograde labeling experiments with cholera toxin B in Pum2; Emx1-Cre and TDP43A315T mice revealed a corresponding increase in subcerebral connectivity of these neurons in S1. Intriguingly, other key features of somatosensory area identity are largely preserved, suggesting that Pum2 and TDP-43 may function in a downstream program, rather than controlling area identity per se. Transfection of primary neurons and in utero electroporation (IUE) suggest cell-autonomous and post-mitotic modulation of Sox5, Bcl11b/Ctip2, and Rorβ levels. Mechanistically, we find that Pum2 and TDP-43 directly interact with and affect the translation of mRNAs encoding Sox5, Bcl11b/Ctip2, and Rorβ. In contrast, effects on the levels of these mRNAs were not detectable in qRT-PCR or single-molecule fluorescent in situ hybridization assays, and we also did not detect effects on their splicing or polyadenylation patterns. Our results support the notion that post-transcriptional regulatory programs involving translational regulation and mediated by Pum2 and TDP-43 contribute to elaboration of area-specific neuronal identity and connectivity in the neocortex.
Keywords: RNA binding proteins; arealization; cell type specification; developmental biology; molecular determinants; mouse; mouse neocortex; neuroscience; translation.
© 2022, Harb et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KH, MR, NN, EM, HH, KK, MH, IH, FC, KD No competing interests declared
Figures





Similar articles
-
Distinct actions of Emx1, Emx2, and Pax6 in regulating the specification of areas in the developing neocortex.J Neurosci. 2002 Sep 1;22(17):7627-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-17-07627.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12196586 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of area-specific expression patterns of RORbeta, ER81 and Nurr1 mRNAs in rat neocortex by double in situ hybridization and cortical box method.PLoS One. 2008 Sep 25;3(9):e3266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003266. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18815614 Free PMC article.
-
BCL11B/CTIP2 is highly expressed in GABAergic interneurons of the mouse somatosensory cortex.J Chem Neuroanat. 2016 Jan;71:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Chem Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 26698402
-
Post-transcriptional regulatory elements and spatiotemporal specification of neocortical stem cells and projection neurons.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 17;248:499-528. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 May 30. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23727006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional co-regulation of neuronal migration and laminar identity in the neocortex.Development. 2012 May;139(9):1535-46. doi: 10.1242/dev.069963. Development. 2012. PMID: 22492350 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The autism susceptibility kinase, TAOK2, phosphorylates eEF2 and modulates translation.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 12;10(15):eadf7001. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf7001. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38608030 Free PMC article.
-
Fate plasticity of interneuron specification.iScience. 2025 Mar 27;28(4):112295. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112295. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40264797 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of adult endogenous neurogenesis by a hyaluronic acid collagen gel containing basic fibroblast growth factor promotes remodeling and functional recovery of the injured cerebral cortex.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Oct 1;20(10):2923-2937. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01706. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39610105 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Post-Transcriptional Regulation in Learning and Memory in Mammals.Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;15(3):337. doi: 10.3390/genes15030337. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gatad2b, associated with the neurodevelopmental syndrome GAND, plays a critical role in neurodevelopment and cortical patterning.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 18;14(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02678-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38238293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold ES, Ling SC, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D, Kordasiewicz HB, McAlonis-Downes M, Platoshyn O, Parone PA, Da Cruz S, Clutario KM, Swing D, Tessarollo L, Marsala M, Shaw CE, Yeo GW, Cleveland DW. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. PNAS. 2013;110:E736–E745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222809110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

