The Impact of COVID-19 Experiences on Adolescent Internalizing Problems and Substance Use Among a Predominantly Latinx Sample
- PMID: 35262825
- PMCID: PMC8905569
- DOI: 10.1007/s10964-022-01593-6
The Impact of COVID-19 Experiences on Adolescent Internalizing Problems and Substance Use Among a Predominantly Latinx Sample
Abstract
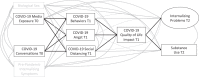
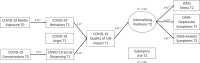
Given the salience of socialization factors on adolescence and their role in vulnerability to disasters and trauma, this study examined whether COVID-19-associated fears and impacted quality of life mediated associations between pandemic-focused family conversations and media exposure and subsequent youth mental health. A primarily Latinx sample of adolescents (N = 167; Mage = 16.2 years, 44.9% female) participated in a longitudinal (summer 2020-winter 2020) COVID-19 study. COVID-19 media exposure predicted engagement in relevant safety behaviors, which negatively impacted quality of life, which in turn predicted increased internalizing problems. COVID-19 family conversations predicted social distancing fears, which negatively impacted quality of life, which then in turn also predicted increased internalizing problems. Targeting key socialization factors may minimize negative consequences following major community trauma among adolescents.
Keywords: COVID-19; Family conversations; Media exposure; Mental health; Quality of life.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
-
- Antony MM, Bieling PJ, Cox BJ, Enns MW, Swinson RP. Psychometric properties of the 42-item and 21-item versions of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales in clinical groups and a community sample. Psychological Assessment. 1998;10(2):176–181. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.10.2.176. - DOI
-
- Ares G, Bove I, Vidal L, Brunet G, Fuletti D, Arroyo A, Blanc MV. The experience of social distancing for families with children and adolescents during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in Uruguay: Difficulties and opportunities. Child and Youth Services Review. 2021;121:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105906. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benke C, Autenrieth LK, Asselmann E, Pane-Farre CA. Lockdown, quarantine measures, and social distancing: Associations with depression, anxiety and distress at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic among adults from Germany. Psychiatry Research. 2020;293:113462. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113462. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

