Pulmonary microbiome and gene expression signatures differentiate lung function in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant candidates
- PMID: 35263147
- PMCID: PMC9487170
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abm8646
Pulmonary microbiome and gene expression signatures differentiate lung function in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant candidates
Abstract
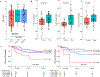
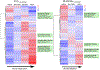
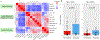
Impaired baseline lung function is associated with mortality after pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), yet limited knowledge of the molecular pathways that characterize pretransplant lung function has hindered the development of lung-targeted interventions. In this study, we quantified the association between bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) metatranscriptomes and paired pulmonary function tests performed a median of 1 to 2 weeks before allogeneic HCT in 104 children in The Netherlands. Abnormal pulmonary function was recorded in more than half the cohort, consisted most commonly of restriction and impaired diffusion, and was associated with both all-cause and lung injury-related mortality after HCT. Depletion of commensal supraglottic taxa, such as Haemophilus, and enrichment of nasal and skin taxa, such as Staphylococcus, in the BAL microbiome were associated with worse measures of lung capacity and gas diffusion. In addition, BAL gene expression signatures of alveolar epithelial activation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and down-regulated immunity were associated with impaired lung capacity and diffusion, suggesting a postinjury profibrotic response. Detection of microbial depletion and abnormal epithelial gene expression in BAL enhanced the prognostic utility of pre-HCT pulmonary function tests for the outcome of post-HCT mortality. These findings suggest a potentially actionable connection between microbiome depletion, alveolar injury, and pulmonary fibrosis in the pathogenesis of pre-HCT lung dysfunction.
Figures
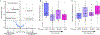


References
-
- D’Souza A, Fretham C, Lee SJ, Aurora M, Brunner J, Chhabra S, Devine S, Eapen M, Hamadani M, Hari P, Pasquini MC, Phelan RA, Riches ML, Rizzo JD, Saber W, Shaw BE, Spellman SR, Steinert P, Weisdorf DJ, Horowitz MM, Current Use and Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in the United States. Biol.Blood Marrow Transplant 26, e177–182 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broglie L, Fretham C, Al-Seraihy A, George B, Kurtzberg J, Loren A, MacMillan M, Martinez C, Davies SM, Pasquini MC, Pulmonary Complications in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 25, 2024–2030 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaya Z, Weiner DJ, Yilmaz D, Rowan J, Goyal RK, Lung function, pulmonary complications, and mortality after allogeneic blood and marrow transplantation in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15, 817–826 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Tamburro RF, Cooke KR, Davies SM, Goldfarb S, Hagood JS, Srinivasan A, Steiner ME, Stokes D, DiFronzo N, El-Kassar N, Shelburne N, Natarajan A, Pulmonary Complications of Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Workshop Participants, Pulmonary Complications of Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HCT): An NIH Workshop Summary. Ann Am Thorac Soc (2020), doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202001-006OT. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duque-Afonso J, Ihorst G, Waterhouse M, Zeiser R, Wäsch R, Bertz H, Yücel M, Köhler T, Müller-Quernheim J, Marks R, Finke J, Comparison of reduced-toxicity conditioning protocols using fludarabine, melphalan combined with thiotepa or carmustine in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 110–120 (2021). - PMC - PubMed

