The IgA in milk induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection is comprised of mainly secretory antibody that is neutralizing and highly durable over time
- PMID: 35263323
- PMCID: PMC8906612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249723
The IgA in milk induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection is comprised of mainly secretory antibody that is neutralizing and highly durable over time
Abstract
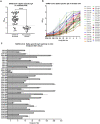
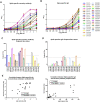
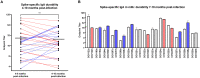
Approximately 10% of infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 will experience COVID-19 illness requiring advanced care. A potential mechanism to protect this population is passive immunization via the milk of a previously infected person. We and others have reported on the presence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in human milk. We now report the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgA in the milk of 74 COVID-19-recovered participants, and find that 89% of samples are positive for Spike-specific IgA. In a subset of these samples, 95% exhibited robust IgA activity as determined by endpoint binding titer, with 50% considered high-titer. These IgA-positive samples were also positive for Spike-specific secretory antibody. Levels of IgA antibodies and secretory antibodies were shown to be strongly positively correlated. The secretory IgA response was dominant among the milk samples tested compared to the IgG response, which was present in 75% of samples and found to be of high-titer in only 13% of cases. Our IgA durability analysis using 28 paired samples, obtained 4-6 weeks and 4-10 months after infection, found that all samples exhibited persistently significant Spike-specific IgA, with 43% of donors exhibiting increasing IgA titers over time. Finally, COVID-19 and pre-pandemic control milk samples were tested for the presence of neutralizing antibodies; 6 of 8 COVID-19 samples exhibited neutralization of Spike-pseudotyped VSV (IC50 range, 2.39-89.4ug/mL) compared to 1 of 8 controls. IgA binding and neutralization capacities were found to be strongly positively correlated. These data are highly relevant to public health, not only in terms of the protective capacity of these antibodies for breastfed infants, but also for the potential use of such antibodies as a COVID-19 therapeutic, given that secretory IgA is highly in all mucosal compartments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of 2143 Pediatric Patients With 2019 Coronavirus Disease in China. Pediatrics. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

