Estimated Life-Years Gained Free of New or Recurrent Major Cardiovascular Events With the Addition of Semaglutide to Standard of Care in People With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 35263432
- PMCID: PMC9174968
- DOI: 10.2337/dc21-1138
Estimated Life-Years Gained Free of New or Recurrent Major Cardiovascular Events With the Addition of Semaglutide to Standard of Care in People With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
Objective: Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a post hoc analysis of pooled data from Trial to Evaluate Cardiovascular and Other Long-term Outcomes with Semaglutide in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN) 6 and Peptide Innovation for Early Diabetes Treatment (PIONEER) 6. We estimated the benefit of adding semaglutide to standard of care (SoC) on life-years free of new/recurrent CVD events in people with T2D at high risk of CVD.
Research design and methods: The Diabetes Lifetime-perspective prediction (DIAL) competing risk-adjusted lifetime CVD risk model for people with T2D was developed previously. Baseline characteristics of the pooled cohort from SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6 (POOLED cohort) (N = 6,480) were used to estimate individual life expectancy free of CVD for patients in the POOLED cohort. The hazard ratio of MACE from adding semaglutide to SoC was derived from the POOLED cohort (hazard ratio [HR] 0.76 [95% CI 0.62-0.92]) and combined with an individual's risk to estimate their CVD benefit.
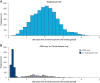
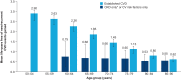
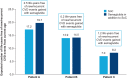
Results: Adding semaglutide to SoC was associated with a wide distribution in life-years free of CVD gained, with a mean increase of 1.7 (95% CI 0.5-2.9) life-years. Estimated life-years free of CVD gained with semaglutide was dependent on baseline risk (life-years free of CVD gained in individuals with established CVD vs. those with cardiovascular risk factors only: 2.0 vs. 0.2) and age at treatment initiation.
Conclusions: Adding semaglutide to SoC was associated with a gain in life-years free of CVD events that was dependent on baseline CVD risk and age at treatment initiation. This study helps contextualize the results of semaglutide clinical trials.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of semaglutide on risk of cardiovascular events across a continuum of cardiovascular risk: combined post hoc analysis of the SUSTAIN and PIONEER trials.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Sep 30;19(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01106-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32998732 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide (SUSTAIN and PIONEER) reduces cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes across varying cardiovascular risk.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Mar;22(3):442-451. doi: 10.1111/dom.13955. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 31903692 Free PMC article.
-
Applying REWIND cardiovascular disease criteria to SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6: An exploratory analysis of cardiovascular outcomes with semaglutide.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021 Jul;23(7):1677-1680. doi: 10.1111/dom.14360. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021. PMID: 33606902 Free PMC article.
-
Oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, renal impairment, or other comorbidities, and in older patients.Postgrad Med. 2020 Nov;132(sup2):37-47. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1800286. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 32815439 Review.
-
Cardiovascular Safety and Benefits of Semaglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Findings From SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 29;12:645566. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.645566. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33854484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous Vasoactive Peptides and Vascular Aging-Related Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 3;2022:1534470. doi: 10.1155/2022/1534470. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36225176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Semaglutide on Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Cardiometabolic Compensation: A Real-World Study in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2023 May 4;11(5):1362. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051362. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239033 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Functional Acceptable Diabetic and Plant-Based Snack Bar Using Mushroom (Coprinus comatus) Powder.Foods. 2023 Jul 14;12(14):2702. doi: 10.3390/foods12142702. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37509794 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide ameliorates cardiac remodeling in male mice by optimizing energy substrate utilization through the Creb5/NR4a1 axis.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 4;15(1):4757. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48970-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38834564 Free PMC article.
-
The time-varying cardiovascular benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Evidence from large multinational trials.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Aug;24(8):1607-1616. doi: 10.1111/dom.14738. Epub 2022 May 23. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35491516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Foundation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th ed. Brussels, International Diabetes Foundation, 2015
-
- Coffey JT, Brandle M, Zhou H, et al. . Valuing health-related quality of life in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25:2238–2243 - PubMed
-
- Hayes A, Arima H, Woodward M, et al. . Changes in quality of life associated with complications of diabetes: results from the ADVANCE study. Value Health 2016;19:36–41 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

