COP1 positively regulates ABA signaling during Arabidopsis seedling growth in darkness by mediating ABA-induced ABI5 accumulation
- PMID: 35263433
- PMCID: PMC9134052
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koac073
COP1 positively regulates ABA signaling during Arabidopsis seedling growth in darkness by mediating ABA-induced ABI5 accumulation
Abstract
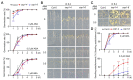
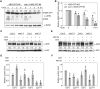
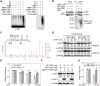
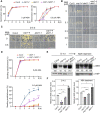
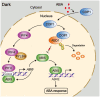
CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 (COP1), a well-characterized E3 ubiquitin ligase, is a central repressor of seedling photomorphogenic development in darkness. However, whether COP1 is involved in modulating abscisic acid (ABA) signaling in darkness remains largely obscure. Here, we report that COP1 is a positive regulator of ABA signaling during Arabidopsis seedling growth in the dark. COP1 mediates ABA-induced accumulation of ABI5, a transcription factor playing a key role in ABA signaling, through transcriptional and post-translational regulatory mechanisms. We further show that COP1 physically interacts with ABA-hypersensitive DCAF1 (ABD1), a substrate receptor of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 ligase targeting ABI5 for degradation. Accordingly, COP1 directly ubiquitinates ABD1 in vitro, and negatively regulates ABD1 protein abundance in vivo in the dark but not in the light. Therefore, COP1 promotes ABI5 protein stability post-translationally in darkness by destabilizing ABD1 in response to ABA. Interestingly, we reveal that ABA induces the nuclear accumulation of COP1 in darkness, thus enhancing its activity in propagating the ABA signal. Together, our study uncovers that COP1 modulates ABA signaling during seedling growth in darkness by mediating ABA-induced ABI5 accumulation, demonstrating that plants adjust their ABA signaling mechanisms according to their light environment.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2022. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



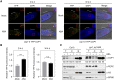
References
-
- Ang LH, Chattopadhyay S, Wei N, Oyama T, Okada K, Batschauer A, Deng XW (1998) Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol Cell 1: 213–222 - PubMed
-
- Bauer D, Viczian A, Kircher S, Nobis T, Nitschke R, Kunkel T, Panigrahi KC, Adam E, Fejes E, Schafer E, et al. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16: 1433–1445 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Li GJ, Bressan RA, Song CP, Zhu JK, Zhao Y (2020) Abscisic acid dynamics, signaling, and functions in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 62: 25–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

