Strategies to Reduce the On-Target Platelet Toxicity of Bcl-xL Inhibitors: PROTACs, SNIPERs and Prodrug-Based Approaches
- PMID: 35263486
- PMCID: PMC9311450
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202100689
Strategies to Reduce the On-Target Platelet Toxicity of Bcl-xL Inhibitors: PROTACs, SNIPERs and Prodrug-Based Approaches
Abstract
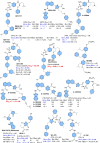
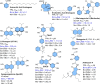
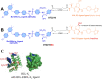
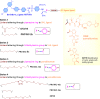
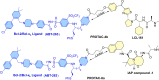
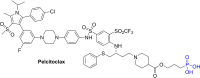
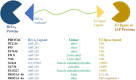
Apoptosis is a highly regulated cellular process. Aberration in apoptosis is a common characteristic of various disorders. Therefore, proteins involved in apoptosis are prime targets in multiple therapies. Bcl-xL is an antiapoptotic protein. Compared to other antiapoptotic proteins, the expression of Bcl-xL is common in solid tumors and, to an extent, in some leukemias and lymphomas. The overexpression of Bcl-xL is also linked to survival and chemoresistance in cancer and senescent cells. Therefore, Bcl-xL is a promising anticancer and senolytic target. Various nanomolar range Bcl-xL inhibitors have been developed. ABT-263 was successfully identified as a Bcl-xL /Bcl-2 dual inhibitor. But it failed in the clinical trial (phase-II) because of its on-target platelet toxicity, which also implies an essential role of Bcl-xL protein in the survival of human platelets. Classical Bcl-xL inhibitor designs utilize occupancy-driven pharmacology with typical shortcomings (such as dose-dependent off-target and on-target platelet toxicities). Hence, event-driven pharmacology-based approaches, such as proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) and SNIPERs (specific non-genetic IAP-based protein erasers) have been developed. The development of Bcl-xL based PROTACs was expected, as 600 E3-ligases are available in humans, while some (such as cereblon (CRBN), von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)) are relatively less expressed in platelets. Therefore, E3 ligase ligand-based Bcl-xL PROTACs (CRBN: XZ424, XZ739; VHL: DT2216, PZ703b, 753b) showed a significant improvement in platelet therapeutic index than their parent molecules (ABT-263: DT2216, PZ703b, 753b, XZ739, PZ15227; A1155463: XZ424). Other than their distinctive pharmacology, PROTACs are molecularly large, which limits their cell permeability and plays a role in improving their cell selectivity. We also discuss prodrug-based approaches, such as antibody-drug conjugates (ABBV-155), phosphate prodrugs (APG-1252), dendrimer conjugate (AZD0466), and glycosylated conjugates (Nav-Gal). Studies of in-vitro, in-vivo, structure-activity relationships, biophysical characterization, and status of preclinical/clinical inhibitors derived from these strategies are also discussed in the review.
Keywords: Bcl-xL; Bcl-xL inhibitors; PROTACs; SNIPERs; drug conjugates; on-target toxicity; platelet toxicity.
© 2022 The Authors. ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

