Deletion of STAT3 from Foxd1 cell population protects mice from kidney fibrosis by inhibiting pericytes trans-differentiation and migration
- PMID: 35263586
- PMCID: PMC10027389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110473
Deletion of STAT3 from Foxd1 cell population protects mice from kidney fibrosis by inhibiting pericytes trans-differentiation and migration
Abstract
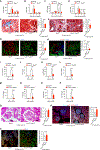
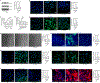
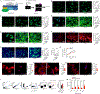
Signal transduction and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a key transcription factor implicated in the pathogenesis of kidney fibrosis. Although Stat3 deletion in tubular epithelial cells is known to protect mice from fibrosis, vFoxd1 cells remains unclear. Using Foxd1-mediated Stat3 knockout mice, CRISPR, and inhibitors of STAT3, we investigate its function. STAT3 is phosphorylated in tubular epithelial cells in acute kidney injury, whereas it is expanded to interstitial cells in fibrosis in mice and humans. Foxd1-mediated deletion of Stat3 protects mice from folic-acid- and aristolochic-acid-induced kidney fibrosis. Mechanistically, STAT3 upregulates the inflammation and differentiates pericytes into myofibroblasts. STAT3 activation increases migration and profibrotic signaling in genome-edited, pericyte-like cells. Conversely, blocking Stat3 inhibits detachment, migration, and profibrotic signaling. Furthermore, STAT3 binds to the Collagen1a1 promoter in mouse kidneys and cells. Together, our study identifies a previously unknown function of STAT3 that promotes kidney fibrosis and has therapeutic value in fibrosis.
Keywords: STAT3; acute kidney injury; chronic kidney disease; fibrosis; inflammation; macrophage infiltration; myofibroblasts transformation; pericytes; stromal cells.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


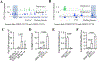
References
-
- Ajay AK, Kim TM, Ramirez-Gonzalez V, Park PJ, Frank DA, and Vaidya VS (2014a). A bioinformatics approach identifies signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and checkpoint kinase 1 as upstream regulators of kidney injury molecule-1 after kidney injury. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 25, 105–118. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ajay AK, Kim TM, Ramirez-Gonzalez V, Park PJ, Frank DA, and Vaidya VS (2014b). A bioinformatics approach identifies signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and checkpoint kinase 1 as upstream regulators of kidney injury molecule-1 after kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 25, 105–118. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anorga S, Overstreet JM, Falke LL, Tang J, Goldschmeding RG, Higgins PJ, and Samarakoon R. (2018). Deregulation of Hippo-TAZ pathway during renal injury confers a fibrotic maladaptive phenotype. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 32, 2644–2657. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artaza JN, Singh R, Ferrini MG, Braga M, Tsao J, and Gonzalez-Cadavid NF (2008). Myostatin promotes a fibrotic phenotypic switch in multipotent C3H 10T1/2 cells without affecting their differentiation into myofibroblasts. J Endocrinol 196, 235–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

