Rates, Variability, and Predictors of Screening for Obesity: Are Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury Being Overlooked?
- PMID: 35263742
- PMCID: PMC9209967
- DOI: 10.1159/000523917
Rates, Variability, and Predictors of Screening for Obesity: Are Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury Being Overlooked?
Abstract
Introduction: Individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI) are vulnerable to obesity. Annual obesity screening using body mass index (BMI) is the standard of care mandated by US Veterans Health Administration (VHA) guidelines. Our objective was to determine the rates, variability, and predictors of guideline-concordant annual screening for obesity, given potential challenges of height and weight measurements in individuals with SCI.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional retrospective study using US national VA databases. We identified all VHA patients with chronic SCI in the fiscal year (FY) 2019, their treating facility and frequency of recorded height and weight. We applied mixed-effects logistic regression models to assess associations between annual BMI screening and patient- and facility-level characteristics.
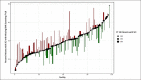
Results: Of 20,978 individuals with chronic SCI in VHA in FY19, guideline-concordant annual BMI screening was lacking in 37.9%. Accounting for facility-level factors (geographic region, SCI facility type, volume of patients with SCI treated at the facility), a mixed-effects logistic regression model demonstrated that lack of annual obesity screening was significantly associated with older patient age (p < 0.001) and fewer outpatient encounters (p < 0.001) but not other patient-level factors such as sex, race, level of injury, or rurality. The rate of obesity screening among different facilities within VHA varied widely from 11.1% to 75.7%.
Conclusion: A large proportion of persons with SCI receiving care in VHA do not receive guideline-concordant annual obesity screening, an especially acute problem in some facilities. Older patients with fewer outpatient encounters are more likely to be missed. To inform the design of interventions to improve identification and documentation of obesity, further study is needed to assess potential barriers to obesity screening in the population with SCI.
Keywords: Obesity; Screening; Spinal cord injury; Veterans.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Why may patients with spinal cord injury be overlooked for obesity screening in the Veterans Health Administration? Qualitative research of the perspectives of patients and healthcare providers.Disabil Rehabil. 2024 Jan;46(2):270-281. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2022.2159074. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Disabil Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 36591701
-
Classification of obesity, cardiometabolic risk, and metabolic syndrome in adults with spinal cord injury.J Spinal Cord Med. 2020 Jul;43(4):485-496. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2018.1557864. Epub 2019 Jan 8. J Spinal Cord Med. 2020. PMID: 30620685 Free PMC article.
-
Health care costs for patients with chronic spinal cord injury in the Veterans Health Administration.J Spinal Cord Med. 2007;30(5):477-81. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2007.11754581. J Spinal Cord Med. 2007. PMID: 18092564 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for classifying obesity in spinal cord injury: a review.Spinal Cord. 2017 Sep;55(9):812-817. doi: 10.1038/sc.2017.79. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Spinal Cord. 2017. PMID: 28695902 Review.
-
Clinical assessment and management of obesity in individuals with spinal cord injury: a review.J Spinal Cord Med. 2008;31(4):361-72. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2008.11760738. J Spinal Cord Med. 2008. PMID: 18959353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of home-based neuromuscular electrical stimulation-resistance training and protein supplementation on lean mass in persons with spinal cord injury: A pilot study.Physiol Rep. 2024 Oct;12(19):e70073. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70073. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358836 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307:491–7. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Flegal KM. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2015;((219)):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282:1523–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

