BET proteins are essential for the specification and maintenance of the epiblast lineage in mouse preimplantation embryos
- PMID: 35264162
- PMCID: PMC8905768
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-022-01251-0
BET proteins are essential for the specification and maintenance of the epiblast lineage in mouse preimplantation embryos
Abstract
Background: During mammalian preimplantation development, as the fertilized egg develops and differentiates, three cell lineages become specified: trophectoderm (TE), epiblast, and primitive endoderm (PrE). Through two steps of cell fate decisions, 16-cell blastomeres develop into TE and an inner cell mass (ICM), and thereafter, the latter differentiates into pluripotent epiblast and PrE. Although bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) proteins, such as BRD4, are necessary for the transcriptional activation of genes involved in the maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells by occupying their enhancers, their roles in the development of mouse preimplantation are unknown.
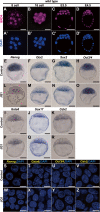
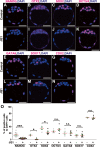
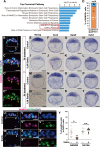
Results: To evaluate the effect of BET protein deficiency on cell lineage formation, we cultured preimplantation embryos in the presence of JQ1, which blocks the binding of BET bromodomains to acetylated-histones. We found BET inhibition blocked the transcriptional activation of genes, such as Nanog, Otx2, and Sox2, important for the formation of the epiblast lineage in blastocysts. Expression studies with lineage-specific markers in morulae and blastocysts revealed BET proteins were essential for the specification and maintenance of the epiblast lineage but were dispensable for the formation of primarily extraembryonic TE and PrE lineages. Additional Ingenuity Pathway Analysis and expression studies with a transcriptionally active form of signal transducer and activator of the transcription 3 (STAT3) suggested BET-dependent activation was partly associated with the STAT3-dependent pathway to maintain the epiblast lineage. To identify BET proteins involved in the formation of the epiblast lineage, we analyzed mutant embryos deficient in Brd4, Brd2, and double mutants. Abolishment of NANOG-positive epiblast cells was only evident in Brd4/Brd2 double-deficient morulae. Thus, the phenotype of JQ1-treated embryos is reproduced not by a Brd4- or Brd2-single deficiency, but only Brd4/Brd2-double deficiency, demonstrating the redundant roles of BRD2 and BRD4 in the specification of the epiblast lineage.
Conclusions: BET proteins are essential to the specification and maintenance of the epiblast lineage by activating lineage-specific core transcription factors during mouse preimplantation development. Among BET proteins, BRD4 plays a central role and BRD2 a complementary role in the specification and maintenance of epiblast lineages. Additionally, BET-dependent maintenance of the epiblast lineage may be partly associated with the STAT3-dependent pathway.
Keywords: BET; Blastocyst; Brd2; Brd4; Bromodomain; Epiblast; Inner cell mass; JQ1; Mouse; Nanog.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

