Visualization of the process of a nanocarrier-mediated gene delivery: stabilization, endocytosis and endosomal escape of genes for intracellular spreading
- PMID: 35264206
- PMCID: PMC8905852
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01336-6
Visualization of the process of a nanocarrier-mediated gene delivery: stabilization, endocytosis and endosomal escape of genes for intracellular spreading
Abstract
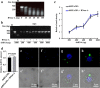
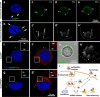
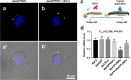
Nanoparticles have been widely applied as gene carrier for improving RNA interference (RNAi) efficiency in medical and agricultural fields. However, the mechanism and delivery process of nanoparticle-mediated RNAi is not directly visualized and elucidated. Here we synthesized a star polymer (SPc) consisted of a hydrophilic shell with positively-charged tertiary amine in the side chain, which was taken as an example to investigate the mechanism in gene delivery. The SPc could assemble with dsRNA spontaneously through electrostatic force, hydrogen bond and van der Waals force. Interestingly, the SPc could protect dsRNA from degradation by RNase A and insect hemolymph, thus remarkably increasing the stability of dsRNA. Meanwhile, the SPc could efficiently promote the cellular uptake and endosomal escape for intracellular spreading of dsRNA. Transcriptome analysis revealed that the SPc could up-regulate some key genes such as Chc, AP2S1 and Arf1 for activating clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Furthermore, the suppression of endocytosis hindered the cellular uptake of SPc-delivered dsRNA in vitro, and the subsequent RNAi effect was also disappeared in vivo. To our knowledge, our study is the first direct visualization of the detailed cellular delivery process and mechanism of nanocarrier-mediated gene delivery. Above mechanism supports the application of nanocarrier-based RNAi in gene therapy and pest management.
Keywords: Cellular uptake; Clathrin; Endocytosis; Nanocarrier; RNA interference; dsRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Van Rij RP, Andino R. The silent treatment: RNAi as a defense against virus infection in mammals. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;24:186–193. - PubMed
-
- Baum JA, Bogaert T, Clinton W, Heck GR, Feldmann P, Ilagan O, Johnson S, Plaetinck G, Munyikwa T, Pleau M, et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Saw PE, Song EW. siRNA therapeutics: A clinical reality. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63:485–500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

