Selective pressure of endocrine therapy activates the integrated stress response through NFκB signaling in a subpopulation of ER positive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 35264224
- PMCID: PMC8908626
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-022-01515-1
Selective pressure of endocrine therapy activates the integrated stress response through NFκB signaling in a subpopulation of ER positive breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: While estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast tumors generally respond well to endocrine therapy (ET), up to 40% of patients will experience relapse, either while on endocrine therapy or after ET is completed. We previously demonstrated that the selective pressure of tamoxifen activates the NFκB pathway in ER + patient tumors, breast cancer cell lines, and breast cancer xenograft tumors, and that this activation allows for survival of a subpopulation of NFκB + cells that contribute to cell regrowth and tumor relapse after ET withdrawal. However, the mechanisms contributing to the expansion of an NFκB + cell population on ET are unknown.
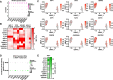
Methods: Here, we utilized single-cell RNA sequencing and bioinformatics approaches to characterize the NFκB + cell population and its clinical relevance. Follow-up studies were conducted to validate our findings and assess the function of the integrated stress response pathway in breast cancer cell lines and patient-derived models.
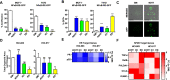
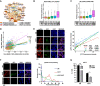
Results: We found that the NFκB + population that arises in response to ET is a preexisting population is enriched under the selective pressure of ET. Based on the preexisting NFκB + cell population, we developed a gene signature and found that it is predictive of tumor relapse when expressed in primary ER + tumors and is retained in metastatic cell populations. Moreover, we identified that the integrated stress response (ISR), as indicated by increased phosphorylation of eIF2α, occurs in response to ET and contributes to clonogenic growth under the selective pressure of ET.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings suggest that a cell population with active NFκB and ISR signaling can survive and expand under the selective pressure of ET and that targeting this population may be a viable therapeutic strategy to improve patient outcome by eliminating cells that survive ET. Understanding the mechanisms by which breast cancer cells survive the selective pressure of ET may improve relapse rates and overall outcome for patients with ER + breast tumors.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Endocrine therapy; Estrogen receptor; Integrated stress response; NFκB.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Novel Strategy to Co-target Estrogen Receptor and Nuclear Factor κB Pathways with Hybrid Drugs for Breast Cancer Therapy.Horm Cancer. 2017 Jun;8(3):135-142. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0294-5. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Horm Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28396978 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced NF kappa B and AP-1 transcriptional activity associated with antiestrogen resistant breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2007 Apr 3;7:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-59. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17407600 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB signaling is important for growth of antiestrogen resistant breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Aug;135(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2053-1. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22527100
-
The NFkappaB pathway and endocrine-resistant breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Jul;12 Suppl 1:S37-46. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00977. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16113098 Review.
-
Update on the Role of NFκB in Promoting Aggressive Phenotypes of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer.Endocrinology. 2020 Oct 1;161(10):bqaa152. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa152. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32887995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-cancer potential of substituted "amino-alkyl-rhodamine" derivatives against MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 May;396(5):1001-1007. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02376-3. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36595094
-
Cysteine dioxygenase 1 attenuates the proliferation via inducing oxidative stress and integrated stress response in gastric cancer cells.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Dec 16;8(1):493. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01277-x. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 36526626 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Key Regulatory Genes in Drug Resistance Acquisition: Modeling Pseudotime Trajectories of Breast Cancer Single-Cell Transcriptome.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 15;16(10):1884. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101884. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791962 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel ER-NFĸB-driven stem-like cell population associated with relapse of ER+ breast tumors.Breast Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 8;24(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01585-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36482488 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells Are More Sensitive to Ceramide Kinase Inhibition and Elevated Ceramide Levels Than Therapy-Sensitive Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 12;14(10):2380. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102380. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu K-D, Wu J, Shen Z-Z, Shao Z-M. Hazard of breast cancer-specific mortality among women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer after five years from diagnosis: implication for extended endocrine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(12):E2201–E2209. - PubMed
-
- Saphner T, Tormey DC, Gray R. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer after primary therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(10):2738–2746. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative G. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

