Endpoint Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Enumeration of Thiocyanate-degrading Bacteria
- PMID: 35264493
- PMCID: PMC8958297
- DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.ME21073
Endpoint Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Enumeration of Thiocyanate-degrading Bacteria
Abstract
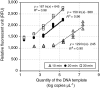
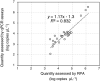
An endpoint recombination amplification reaction (RPA) assay for assessing the abundance of the gene encoding thiocyanate dehydrogenase (TcDH) in Thiohalobacter has been developed. The RPA reaction was performed at 37°C for 30 min, terminated by the addition of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution, and the DNA concentration of the RPA product was fluorometrically measured. The abundance of TcDH in 22 activated sludge samples and 7 thiocyanate-degrading enrichment cultures ranged between 2.5×103 and 1.5×106 copies μL-1, showing a linear relationship (R2=0.83) with those measured using a conventional quantitative PCR assay.
Keywords: endpoint assay; gene quantification; recombination amplification reaction (RPA); thiocyanate dehydrogenase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and evaluation of real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid and sensitive detection of Vibro mimicus in human plasma samples.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Sep;133(3):1650-1659. doi: 10.1111/jam.15666. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35702884
-
Rapid detection of the New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) gene by recombinase polymerase amplification.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Jan;87:104678. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104678. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 33321225
-
Thiocyanate Degradation by a Highly Enriched Culture of the Neutrophilic Halophile Thiohalobacter sp. Strain FOKN1 from Activated Sludge and Genomic Insights into Thiocyanate Metabolism.Microbes Environ. 2019 Dec 27;34(4):402-412. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME19068. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Microbes Environ. 2019. PMID: 31631078 Free PMC article.
-
[Preliminary application of real-time fluorescence recombinase polymerase amplification in Candida albicans].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019 Aug 20;35(8):587-594. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.08.006. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31474038 Chinese.
-
Rapid detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) by recombinase polymerase amplification.J Virol Methods. 2022 Feb;300:114362. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114362. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Virol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34801595
Cited by
-
A rapid and visual detection assay for Clonorchis sinensis based on recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow dipstick.Parasit Vectors. 2023 May 19;16(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05774-5. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37208693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoi, Y., Hosogai, M., and Tsuneda, S. (2006) Real-time quantitative LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA) as a simple method for monitoring ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Biotechnol 125: 484–491. - PubMed
-
- Crannell, Z., Castellanos-Gonzalez, A., Nair, G., Mejia, R., and White, A.C. (2016) Multiplexed recombinase polymerase amplification assay to detect intestinal protozoa. Anal Chem 88: 1610–1616. - PubMed
-
- da Silva, A.K., Le Saux, J-C., Parnaudeau, S., Pommepuy, M., Elimelech, M., and Le Guyader, F.S. (2007) Evaluation of removal of noroviruses during wastewater treatment, using real-time reverse transcription-PCR: different behaviors of genogroups I and II. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 7891–7897. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dionisi, H.M., Layton, A.C., Harms, G., Gregory, I.R., Robinson, K.G., and Sayler, G.S. (2002) Quantification of Nitrosomonas oligotropha-like ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and Nitrospira spp. from full-scale wastewater treatment plants by competitive PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 245–253. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harms, G., Layton, A.C., Dionisi, H.M., Gregory, I.R., Garrett, V.M., Hawkins, S.A., et al. (2003) Real-time PCR quantification of nitrifying bacteria in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 37: 343–351. - PubMed

