An enhancer variant at 16q22.1 predisposes to hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating PRMT7 expression
- PMID: 35264579
- PMCID: PMC8907293
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28861-0
An enhancer variant at 16q22.1 predisposes to hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating PRMT7 expression
Abstract
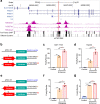
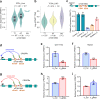
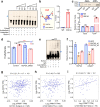
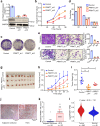
Most cancer causal variants are found in gene regulatory elements, e.g., enhancers. However, enhancer variants predisposing to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unreported. Here we conduct a genome-wide survey of HCC-susceptible enhancer variants through a three-stage association study in 11,958 individuals and identify rs73613962 (T > G) within the intronic region of PRMT7 at 16q22.1 as a susceptibility locus of HCC (OR = 1.41, P = 6.02 × 10-10). An enhancer dual-luciferase assay indicates that the rs73613962-harboring region has allele-specific enhancer activity. CRISPR-Cas9/dCas9 experiments further support the enhancer activity of this region to regulate PRMT7 expression. Mechanistically, transcription factor HNF4A binds to this enhancer region, with preference to the risk allele G, to promote PRMT7 expression. PRMT7 upregulation contributes to in vitro, in vivo, and clinical HCC-associated phenotypes, possibly by affecting the p53 signaling pathway. This concept of HCC pathogenesis may open a promising window for HCC prevention/treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Montalto G, et al. Epidemiology, risk factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2002;963:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:755–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

