Detection of germline variants in Brazilian breast cancer patients using multigene panel testing
- PMID: 35264596
- PMCID: PMC8907244
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-07383-1
Detection of germline variants in Brazilian breast cancer patients using multigene panel testing
Abstract
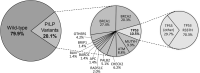
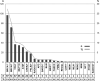
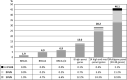
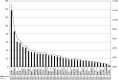
Genetic diversity of germline variants in breast cancer (BC) predisposition genes is unexplored in miscegenated populations, such those living in Latin America. We evaluated 1663 Brazilian BC patients, who underwent hereditary multigene panel testing (20-38 cancer susceptibility genes), to determine the spectrum and prevalence of pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants and variants of uncertain significance (VUS). Associations between P/LP variants and BC risk were estimated in a case-control analysis of BC patients and 18,919 Brazilian reference controls (RC). In total, 335 (20.1%) participants carried germline P/LP variants: 167 (10.0%) in BRCA1/2, 122 (7.3%) in BC actionable non-BRCA genes and 47 (2.8%) in candidate genes or other cancer predisposition genes. Overall, 354 distinctive P/LP variants were identified in 23 genes. The most commonly mutated genes were: BRCA1 (27.4%), BRCA2 (20.3%), TP53 (10.5%), monoallelic MUTYH (9.9%), ATM (8.8%), CHEK2 (6.2%) and PALB2 (5.1%). The Brazilian variant TP53 R337H (c.1010G>A, p.Arg337His), detected in 1.6% of BC patients and 0.1% of RC, was strongly associated with risk of BC, OR = 17.4 (95% CI: 9.4-32.1; p < 0.0001); monoallelic MUTYH variants c.1187G>A and c.536A>G, detected in 1.2% (0.9% RC) and 0.8% (0.4% RC) of the patients, respectively, were not associated with the odds of BC, the former with OR = 1.4 (95% CI: 0.8-2.4; p = 0.29) and the latter with OR = 1.9 (95% CI: 0.9-3.9; p = 0.09). The overall VUS rate was 46.1% for the entire patient population. Concluding, the use of multigene panel testing almost doubled the identification of germline P/LP variants in clinically actionable predisposition genes in BC patients. In Brazil, special attention should be given to TP53 P/LP variants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Founders and employees of Mendelics Análise Genômica served as coinvestigators in this study and provided material support, including germline testing and interpretation, as described in the manuscript. The specific coinvestigators listed as authors participated in the review and final approval of the submitted manuscript. R.S.C.G. acted as a consultant for AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline and Igenomix; received speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Sharpe & Dohme Brasil, Novartis, and Roche outside the submitted work; and has equity in Mendelics Análise Genômica. J.P.F.W.K., A.V., D.S. and F.K. are co-founders at Mendelics Análise Genômica. O.I.O. is co-founder at CancerIQ; serves as scientific advisor at Tempus; and is on the advisory board of 54gene. All the other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ministério da Saúde. Instituto Nacional de Câncer José Alencar Gomes da Silva. Estimativa 2020: Incidência de câncer no Brasil. https://www.inca.gov.br/sites/ufu.sti.inca.local/files//media/document//... (2019).
-
- Kurian AW, et al. Breast and ovarian cancer penetrance estimates derived from germline multiple-gene sequencing results in women. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017;1:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen FC, van Overeem Hansen T, Sørensen CS. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer: New genes in confined pathways. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:599–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

