Hepcidin in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35264787
- PMCID: PMC9296449
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-022-01753-2
Hepcidin in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
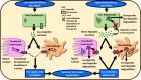
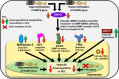
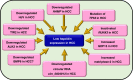
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common reasons for cancer-related deaths. Excess iron increases HCC risk. Inevitably, hepcidin, the iron hormone that maintains systemic iron homoeostasis is involved in HCC pathology. Distinct from other cancers that show high hepcidin expression, HCC patients can show low hepcidin levels. Thus, it is of immense clinical benefit to address the regulation and action of hepcidin in HCC as this may help in identifying molecular targets for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics. Accordingly, this review explores hepcidin in HCC. It presents the levels of tissue and serum hepcidin and explains the mechanisms that contribute to hepcidin reduction in HCC. These include downregulation of HAMP, TfR2, HJV, ALK2 and circular RNA circ_0004913, upregulation of matriptase-2 and GDF15, inactivation of RUNX3 and mutation in TP53. The enigmas around mir-122 and the functionalities of two major hepcidin inducers BMP6 and IL6 in relation to hepcidin in HCC are discussed. Effects of hepcidin downregulation are explained, specifically, increased cancer proliferation via activation of CDK1/STAT3 pathway and increased HCC risk due to reduction in a hepcidin-mediated protective effect against hepatic stellate cell activation. Hepcidin-ferroportin axis in HCC is addressed. Finally, the role of hepcidin in the diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutics of HCC is highlighted.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

