Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 35264932
- PMCID: PMC8900732
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.832854
Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
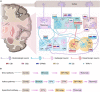
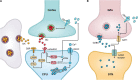
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease usually caused by neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and other etiologies. Recent studies have found that the cannabinoid system present in the basal ganglia has a strong influence on the progression of PD. Altering the cannabinoid receptor activation status by modulating endogenous cannabinoid (eCB) levels can exert an anti-movement disorder effect. Therefore, the development of drugs that modulate the endocannabinoid system may be a novel strategy for the treatment of PD. However, eCB regulation is complex, with diverse cannabinoid receptor functions and the presence of dopaminergic, glutamatergic, and γ-aminobutyric signals interacting with cannabinoid signaling in the basal ganglia region. Therefore, the study of eCB is challenging. Here, we have described the function of the cannabinoid system in the basal ganglia and its association with PD in three parts (eCBs, cannabinoid receptors, and factors regulating the cannabinoid metabolism) and summarized the mechanisms of action related to the cannabinoid analogs currently aimed at treating PD. The shortcomings identified from previous studies and the directions that should be explored in the future will provide insights into new approaches and ideas for the future development of cannabinoid-based drugs and the treatment of PD.
Keywords: CB1 receptors; CB2 receptors; Parkinson’s disease; basal ganglia; cannabinoids.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 9;16:897930. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.897930. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35614972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abdel-Salam O. M. E., Youness E. R., Khadrawy Y. A., Mohammed N. A., Abdel-Rahman R. F., Omara E. A., et al. (2015). The effect of cannabis on oxidative stress and neurodegeneration induced by intrastriatal rotenone injection in rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 24 359–378. 10.1007/s00580-014-1907-9 - DOI
-
- Aguilera-Portillo G., Rangel-Lopez E., Villeda-Hernandez J., Chavarria A., Castellanos P., Elmazoglu Z., et al. (2019). The pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase prevents excitotoxic damage in the rat striatum: possible involvement of CB1 receptors regulation. Mol. Neurobiol. 56 844–856. 10.1007/s12035-018-1129-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

