Clinical Correlates Identify ProBDNF and Thrombo-Inflammatory Markers as Key Predictors of Circulating p75NTR Extracellular Domain Levels in Older Adults
- PMID: 35264944
- PMCID: PMC8899540
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.821865
Clinical Correlates Identify ProBDNF and Thrombo-Inflammatory Markers as Key Predictors of Circulating p75NTR Extracellular Domain Levels in Older Adults
Abstract
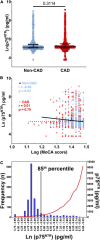
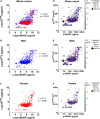
The p75NTR receptor binds all neurotrophins and is mostly known for its role in neuronal survival and apoptosis. Recently, the extracellular domain (ECD) of p75NTR has been reported in plasma, its levels being dysregulated in numerous neurological diseases. However, the factors associated with p75NTR ECD levels remain unknown. We investigated clinical correlates of plasma p75NTR ECD levels in older adults without clinically manifested neurological disorders. Circulating p75NTR levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in plasma obtained from participants in the BEL-AGE cohort (n = 1,280). Determinants of plasma p75NTR ECD levels were explored using linear and non-linear statistical models. Plasma p75NTR ECD levels were higher in male participants; were positively correlated with circulating concentrations of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and inflammatory markers interleukin-6 and CD40 Ligand; and were negatively correlated with the platelet activation marker P-selectin. While most individuals had p75NTR levels ranging from 43 to 358 pg/ml, high p75NTR levels reaching up to 9,000 pg/ml were detectable in a subgroup representing 15% of the individuals studied. In this cohort of older adults without clinically manifested neurological disorders, there was no association between plasma p75NTR ECD levels and cognitive performance, as assessed by the Montreal Cognitive Assessment score. The physiological relevance of high p75NTR ECD levels in plasma warrants further investigation. Further research assessing the source of circulating p75NTR is needed for a deeper understanding of the direction of effect, and to investigate whether high p75NTR ECD levels are predictive biomarkers or consequences of neuropathology.
Keywords: inflammation; neurotrophhic factors; p75NTR receptor; plasma; proBDNF.
Copyright © 2022 Fleury, Schnitzer, Ledoux-Hutchinson, Boukhatem, Bélanger, Welman, Busseuil, Tardif, D’Antono and Lordkipanidzé.
Conflict of interest statement
ML has received speaker fees from Bayer; has participated in industry-funded trials from Idorsia; has served on advisory boards for Servier and JAMP/Orimed Pharma; and has received in-kind and financial support for investigator-initiated grants from Leo Pharma, Roche Diagnostics, Aggredyne, and Fujimori Kogyo. MS has received speaker fees from Biogen and consultant fees from Carebook Technologies Inc. J-CT reports research grants from Amarin, AstraZeneca, Ceapro, DalCor Pharmaceuticals, Esperion, Ionis, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi; honoraria from AstraZeneca, DalCor Pharmaceuticals, HLS Pharmaceuticals, and Pendopharm; and minor equity interest in DalCor Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble p75 neurotrophic receptor as a reliable biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases: what is the evidence?Neural Regen Res. 2024 Mar;19(3):536-541. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.380873. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37721281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-Regulation of ProBDNF/p75NTR Signaling in Spinal Cord Drives Inflammatory Pain in Male Rats.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Jan 9;16:95-107. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S387127. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36643954 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of proBDNF/p75NTR in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with sepsis and its impact on lymphocyte differentiation.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Nov 28;48(11):1629-1638. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230179. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38432853 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
The p75 neurotrophin receptor might mediate sepsis-induced synaptic and cognitive impairments.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Jul 16;347:339-349. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.03.042. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29604364
-
Death domain of p75 neurotrophin receptor: a structural perspective on an intracellular signalling hub.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019 Aug;94(4):1282-1293. doi: 10.1111/brv.12502. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019. PMID: 30762293 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble p75 neurotrophic receptor as a reliable biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases: what is the evidence?Neural Regen Res. 2024 Mar;19(3):536-541. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.380873. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37721281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

