Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Excretion Characteristics of a Radix Polygoni Multiflori Extract in Rats
- PMID: 35264960
- PMCID: PMC8899820
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.827668
Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Excretion Characteristics of a Radix Polygoni Multiflori Extract in Rats
Abstract
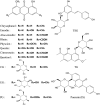
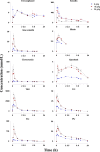
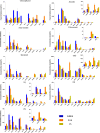
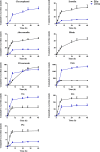
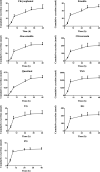
Although progress has been achieved in the pharmacological activity and toxicity of Radix Polygoni Multiflori (RPM), the chemical basis of its toxicity is still unclear. Here, we performed a multicompound pharmacokinetic analysis and investigated the tissue distribution and excretion characteristics of RPM components after oral administration in rats. The findings demonstrated that the active ingredients of the RPM extract were quickly absorbed after oral administration, with high exposure levels of emodin, 2,3,5,4'-teterahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside (TSG), citreorosein, torachrysone-8-O-glucoside (TG), emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside (EG), and physcion-8-O-β-D-glucoside (PG). The tissue distributions of emodin, TSG, TG, EG, and PG were high in the liver and kidney. These components were the key contributors to the effectiveness and toxicity of RPM on the liver and kidney. Most of the active ingredients were mainly excreted through feces and bile, while a few were converted into other products in the body and excreted through urine and feces.
Keywords: Radix Polygoni Multiflori; UPLC-MS/MS; excretion; pharmacokinetics; tissue distribution.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Wu, Yuan, Hu, Yu, Kang, Wang, Zhu, Xia, Yang, Kang, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatoxicity of major constituents and extractions of Radix Polygoni Multiflori and Radix Polygoni Multiflori Praeparata.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 11;137(3):1291-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.055. Epub 2011 Aug 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21840387
-
Simultaneous Determination of 13 Constituents of Radix Polygoni Multiflori in Rat Plasma and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study.Int J Anal Chem. 2020 Mar 3;2020:4508374. doi: 10.1155/2020/4508374. eCollection 2020. Int J Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32190053 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the protection of water extracts of Polygoni Multiflori Radix and Polygoni Multiflori Radix Praeparata against NAFLD and its mechanism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 24;252:112577. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112577. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31953200
-
Overview of Pharmacokinetics and Liver Toxicities of Radix Polygoni Multiflori.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 21;12(11):729. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110729. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33233441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotection and hepatotoxicity of Heshouwu, a Chinese medicinal herb: Context of the paradoxical effect.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Oct;108(Pt B):407-418. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.07.035. Epub 2016 Jul 30. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27484243 Review.
Cited by
-
Measurement of Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Four Compounds from Nauclea officinalis in Rat Plasma and Tissues through HPLC-MS/MS.J Anal Methods Chem. 2022 Dec 21;2022:5297603. doi: 10.1155/2022/5297603. eCollection 2022. J Anal Methods Chem. 2022. PMID: 36591325 Free PMC article.
-
Idiosyncratic liver injury induced by bolus combination treatment with emodin and 2,3,5,4'-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1017741. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1017741. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36225587 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds.Molecules. 2024 Aug 14;29(16):3845. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163845. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202924 Free PMC article.
-
A Network-Pharmacology-Combined Integrated Pharmacokinetic Strategy to Investigate the Mechanism of Potential Liver Injury due to Polygonum multiflorum.Molecules. 2022 Dec 6;27(23):8592. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238592. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500685 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-component pharmacokinetic study of prunus mume fructus extract after oral administration in rats using UPLC-MS/MS.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 23;13:954692. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.954692. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Büchter C., Zhao L., Havermann S., Honnen S., Fritz G., Proksch P., et al. (2015). TSG (2,3,5,4'-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O- β -D-Glucoside) from the Chinese Herb Polygonum Multiflorum Increases Life Span and Stress Resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans . Oxid. Med. Cel. Longev. 2015, 124357. 10.1155/2015/124357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang Y. X., Ge A. H., Jiang Y., Teye Azietaku J., Li J., Gao X. M. (2016). A Bioactivity-Based Method for Screening, Identification of Lipase Inhibitors, and Clarifying the Effects of Processing Time on Lipase Inhibitory Activity of Polygonum Multiflorum. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2016, 5965067. 10.1155/2016/5965067 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Q., Zhang S.-z., Ying H.-z., Dai X.-y., Li X.-x., Yu C.-h., et al. (2012). Chemical Characterization and Immunostimulatory Effects of a Polysaccharide from Polygoni Multiflori Radix Praeparata in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Anemic Mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 88 (4), 1476–1482. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.055 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

