The Bioflavonoids Rutin and Rutin Succinate Neutralize the Toxins of B. jararaca Venom and Inhibit its Lethality
- PMID: 35264963
- PMCID: PMC8899467
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.828269
The Bioflavonoids Rutin and Rutin Succinate Neutralize the Toxins of B. jararaca Venom and Inhibit its Lethality
Abstract
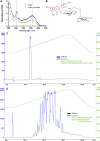
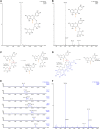
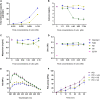
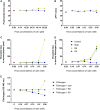
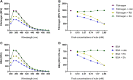
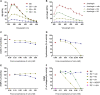
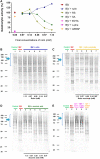
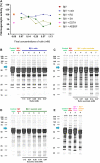
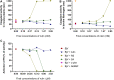
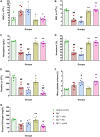
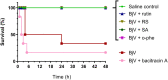
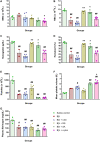
The venom of the Brazilian pit viper Bothrops jararaca (BjV) is a complex mixture of molecules, and snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMP) and serine proteinases (SVSP) are the most abundant protein families found therein. Toxins present in BjV trigger most of the deleterious disturbances in hemostasis observed in snakebites, i.e., thrombocytopenia, hypofibrinogenemia and bleedings. The treatment of patients bitten by snakes still poses challenges and the bioflavonoid rutin has already been shown to improve hemostasis in an experimental model of snakebite envenomation. However, rutin is poorly soluble in water; in this study, it was succinylated to generate its water-soluble form, rutin succinate (RS), which was analyzed comparatively regarding the chemical structure and characteristic features of rutin. Biological activities of rutin and RS were compared on hemostatic parameters, and against toxic activities of crude BjV in vitro. In vivo, C57BL/6 mice were injected i.p. with either BjV alone or pre-incubated with rutin, RS or 1,10-phenanthroline (o-phe, an SVMP inhibitor), and the survival rates and hemostatic parameters were analyzed 48 h after envenomation. RS showed the characteristic activities described for rutin - i.e., antioxidant and inhibitor of protein disulfide isomerase - but also prolonged the clotting time of fibrinogen and plasma in vitro. Differently from rutin, RS inhibited typical proteolytic activities of SVMP, as well as the coagulant activity of BjV. Importantly, both rutin and RS completely abrogated the lethal activity of BjV, in the same degree as o-phe. BjV induced hemorrhages, falls in RBC counts, thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenemia in mice. Rutin and RS also improved the recovery of platelet counts and fibrinogen levels, and the development of hemorrhages was totally blocked in mice injected with BjV incubated with RS. In conclusion, RS has anticoagulant properties and is a novel SVMP inhibitor. Rutin and RS showed different mechanisms of action on hemostasis. Only RS inhibited directly BjV biological activities, even though both flavonoids neutralized B. jararaca toxicity in vivo. Our results showed clearly that rutin and RS show a great potential to be used as therapeutic compounds for snakebite envenomation.
Keywords: antivenom; coagulation; hemostasis; rutin; snake venom.
Copyright © 2022 Sachetto, Miyamoto, Tashima, de Souza and Santoro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

