LIMK1 Interacts with STK25 to Regulate EMT and Promote the Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 35265128
- PMCID: PMC8901301
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3963883
LIMK1 Interacts with STK25 to Regulate EMT and Promote the Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
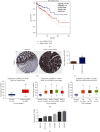
Objective: To investigate the interaction between LIMK1 and STK25 and its expression in colon cancer and its effect on the malignant evolution of colon cancer.
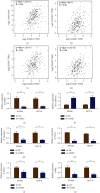
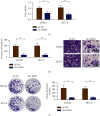
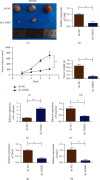
Methods: Fluorescence quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to detect the expression of the LIMK1 gene in cancer and adjacent tissues of 20 clinical colon cancer samples. The overexpression plasmids of LIMK1 and STK25 were constructed. An shRNA specific to LIMK1 was synthesized and transfected into colon cancer cell lines. The expression levels of EMT-related markers in cell lines were detected by real-time PCR. The effects of LIMK1 and STK25 on the proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cell lines were detected by CCK-8 assay, Transwell, and clonogenesis.
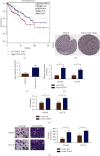
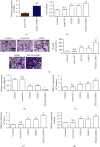
Results: LIMK1 interacted with STK25 and was highly expressed in colon cancer. High expression of LIMK1 and STK25 is associated with poor prognosis in colon cancer patients. LIMK silencing inhibits proliferation, invasion, and EMT of colon cancer. Cotransfection of LIMK1 and STK25 promotes the malignant progression and EMT of colon cancer.
Conclusion: Protein interaction between LIMK1 and STK25 occurs. Overexpression of LIMK1 and STK25 plays a role in promoting cell proliferation and invasion in colon cancer tissues and cells. They also play a role in promoting the occurrence and development of colon cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Xuecheng Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
STK25 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression through the STRN/AMPK/ACC1 pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jan 5;22(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02421-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 34986838 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 signaling pathway on proliferation, invasion, and migration of human osteosarcoma cells.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Sep;34(9):e23362. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23362. Epub 2020 May 28. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32463132 Free PMC article.
-
PTPN6-EGFR Protein Complex: A Novel Target for Colon Cancer Metastasis.J Oncol. 2022 Feb 11;2022:7391069. doi: 10.1155/2022/7391069. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35186080 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27b-3p suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting LIMK1 in colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Sep 1;10(9):9251-9261. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966797 Free PMC article.
-
LIM kinase 1 interacts with myosin-9 and alpha-actinin-4 and promotes colorectal cancer progression.Br J Cancer. 2017 Aug 8;117(4):563-571. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.193. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28664914 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel Histopathological Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer: Implications and Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2023 May 26;11(6):1552. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061552. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Impacts of Striatins and the STRIPAK Complex and Their Roles in the Development and Metastasis in Clinical Cancers (Review).Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;16(1):76. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010076. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Five Tumor Antigens for Development and Two Immune Subtypes for Personalized Medicine of mRNA Vaccines in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 18;13(2):359. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020359. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836593 Free PMC article.
-
PDZ and LIM Domain-Encoding Genes: Their Role in Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):5042. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205042. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grasso C. S., Giannakis M., Wells D. K., et al. Genetic mechanisms of immune evasion in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discovery . 2018;8(6):730–749. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.cd-17-1327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

