Lactobacillus helveticus Prevents Periodontitis Induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in Rats by Regulating β-Defensins
- PMID: 35265172
- PMCID: PMC8898852
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4968016
Lactobacillus helveticus Prevents Periodontitis Induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in Rats by Regulating β-Defensins
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Lactobacillus helveticus Prevents Periodontitis Induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in Rats by Regulating β-Defensins.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9816032. doi: 10.1155/2023/9816032. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811205 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To study the preventive effect of Lactobacillus helveticus (L. helveticus) on periodontitis induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (A. actinomycetemcomitans) in rats.
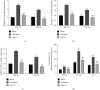
Methods: Eighteen 8-week-old female rats were randomly divided into three groups: Sham group, Trehalose group, and L. helveticus SBT2171 (LH2171) group. We measured the distance of the cementoenamel junction-alveolar bone crest (CEJ-ABC) to evaluate alveolar bone resorption. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to observe the histopathological changes of rat hemimaxillary tissues. We detected the expression of β-defensins, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin- (IL-) 1β, and IL-6 and the number of A. actinomycetemcomitans in rat gingival tissues by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in rat gingival tissues were also measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
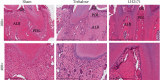
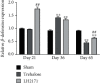
Results: Compared with the Trehalose group, the distance of CEJ-ABC was prominently reduced and alveolar bone resorption was notably improved in the LH2171 group. And the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the hemimaxillary tissue decreased obviously, periodontal fibers were arranged neatly, connective tissue small blood vessels proliferated, and the number of A. actinomycetemcomitans reduced significantly in the LH2171 group. In addition, the mRNA expression and release of inflammatory factors in the gingival tissues in the LH2171 group were notably lower than those in the Trehalose group. On the 21st and 36th day, the expression of β-defensins in the gingival tissue of the LH2171 group increased significantly.
Conclusion: L. helveticus improves alveolar bone resorption and increases the expression of β-defensins thereby inhibiting the number of A. actinomycetemcomitans and thus prevents periodontitis.
Copyright © 2022 Ru Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus helveticus SBT2171 upregulates the expression of β-defensin and ameliorates periodontal disease caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis.Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Aug;63(8):293-302. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12719. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31209914
-
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide-mediated experimental bone loss model for aggressive periodontitis.J Periodontol. 2007 Mar;78(3):550-8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2007.060321. J Periodontol. 2007. PMID: 17335380 Free PMC article.
-
Nootkatone mitigates periodontal inflammation and reduces alveolar bone loss via Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways in rat model of periodontitis.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2024;62(3):145-153. doi: 10.5603/fhc.101862. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2024. PMID: 39192685
-
The Histone Demethylase Inhibitor GSK-J4 Attenuates Periodontal Bone Loss and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Periodontitis.Curr Med Sci. 2025 Apr;45(2):382-390. doi: 10.1007/s11596-025-00018-2. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Curr Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40048054
-
O-Polysaccharide Plays a Major Role on the Virulence and Immunostimulatory Potential of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans During Periodontal Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 30;11:591240. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.591240. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of systemic Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus probiotics on the ligature-induced periodontitis in rat.J Dent Sci. 2023 Oct;18(4):1477-1485. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.04.013. Epub 2023 May 5. J Dent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37799895 Free PMC article.
-
Host mRNA Analysis of Periodontal Disease Patients Positive for Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Tannerella forsythia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 31;23(17):9915. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179915. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Functional Properties of Dairy Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 11;11(7):1787. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071787. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retracted: Lactobacillus helveticus Prevents Periodontitis Induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in Rats by Regulating β-Defensins.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9816032. doi: 10.1155/2023/9816032. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lakhssassi N., Elhajoui N., Lodter J. P., Pineill J. L., Sixou M. Antimicrobial susceptibility variation of 50 anaerobic periopathogens in aggressive periodontitis: an interindividual variability study. Oral Microbiology and Immunology . 2005;20(4):244–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2005.00225.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

