Claudin-5 binder enhances focused ultrasound-mediated opening in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
- PMID: 35265192
- PMCID: PMC8899584
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.65539
Claudin-5 binder enhances focused ultrasound-mediated opening in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
Abstract
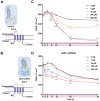
Rationale: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) while functioning as a gatekeeper of the brain, impedes cerebral drug delivery. An emerging technology to overcome this limitation is focused ultrasound (FUS). When FUS interacts with intravenously injected microbubbles (FUS+MB), the BBB opens, transiently allowing the access of therapeutic agents into the brain. However, the ultrasound parameters need to be tightly tuned: when the acoustic pressure is too low there is no opening, and when it is too high, tissue damage can occur. We therefore asked whether barrier permeability can be increased by combining FUS+MB with a second modality such that in a clinical setting lower acoustic pressures could be used. Methods: Given that FUS+MB achieves BBB opening in part by disruption of tight junction (TJ) proteins such as claudin-5 of brain endothelial cells, we generated a stable MDCK (Madin-Darby Canine Kidney) II cell line (eGFP-hCldn5-MDCK II) that expresses fluorescently tagged human claudin-5. Two claudin-5 binders, the peptide mC5C2 and cCPEm (truncated form of an enterotoxin), reported previously to weaken the barrier, were synthesized and assessed for their abilities to enhance the permeability of cellular monolayers. We then performed a comparative analysis of single and combination treatments, measuring transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) and cargo leakage, combined with confocal image analysis. Results: We successfully generated a novel cell line that formed functional monolayers as validated by an increased TEER reading and a low (< 0.2%) permeability to sodium fluorescein (376 Da). We found that the binders exerted a time- and concentration-dependent effect on barrier opening when incubated over an extended period, whereas FUS+MB caused a rapid opening followed by recovery after 12 hours within the tested pressure range. Importantly, preincubation with cCPEm prior to FUS+MB treatment resulted in greater barrier opening compared to either FUS+MB or cCPEm alone as measured by reduced TEER values and an increased permeability to fluorescently labelled 40 kDa dextran (FD40). Conclusion: The data suggest that pre incubation with clinically suitable binders to TJ proteins may be a general strategy to facilitate safer and more effective ultrasound-mediated BBB opening in cellular and animal systems and potentially also for the treatment of human diseases of the brain.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier (BBB); claudin-5; focused ultrasound; transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Multimodal evaluation of blood-brain barrier opening in mice in response to low-intensity ultrasound and a claudin-5 binder.Nanotheranostics. 2024 Apr 23;8(4):427-441. doi: 10.7150/ntno.95146. eCollection 2024. Nanotheranostics. 2024. PMID: 38961889 Free PMC article.
-
A patient-derived amyotrophic lateral sclerosis blood-brain barrier model for focused ultrasound-mediated anti-TDP-43 antibody delivery.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Aug 13;21(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00565-1. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39138578 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil recruitment and leukocyte response following focused ultrasound and microbubble mediated blood-brain barrier treatments.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(4):1655-1671. doi: 10.7150/thno.52710. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33408773 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the safety profile of focused ultrasound and microbubble-mediated treatments to increase blood-brain barrier permeability.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Feb;16(2):129-142. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1567490. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30628455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Focused Ultrasound-mediated Drug Delivery in Humans - a Path Towards Translation in Neurodegenerative Diseases".Pharm Res. 2022 Mar;39(3):427-439. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03185-2. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35257286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of an L-Valine-Modified Nanomicelle-Based Drug Delivery System for Overcoming Ocular Surface Barriers.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 16;14(6):1277. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061277. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745853 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-pore model of the blood-brain barrier tight junction strands recapitulates the permeability features of wild-type and mutant claudin-5.Protein Sci. 2025 Sep;34(9):e70271. doi: 10.1002/pro.70271. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40862374 Free PMC article.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by driving Th1 differentiation via ZAP70/NF-κB signaling.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 18;16:1549102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549102. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40170858 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease brain endothelial-like cells reveal differential drug transporter expression and modulation by potentially therapeutic focused ultrasound.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Jan;21(1):e00299. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2023.10.009. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 38241156 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in BBB on Chip and Application for Studying Reversible Opening of Blood-Brain Barrier by Sonoporation.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;14(1):112. doi: 10.3390/mi14010112. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36677173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banks WA. From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Dscov. 2016;15:275–92. - PubMed
-
- Hynynen K, McDannold N, Vykhodtseva N, Jolesz FA. Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology. 2001;220:640–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

