Non-invasive photobiomodulation treatment in an Alzheimer Disease-like transgenic rat model
- PMID: 35265207
- PMCID: PMC8899582
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.70756
Non-invasive photobiomodulation treatment in an Alzheimer Disease-like transgenic rat model
Abstract
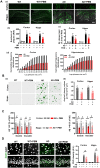
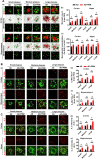
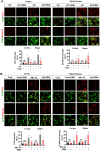
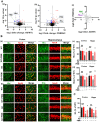
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly, causing neuronal degeneration and cognitive deficits that significantly impair independence and quality of life for those affected and their families. Though AD is a major neurodegenerative disease with vast avenues of investigation, there is no effective treatment to cure AD or slow disease progression. The present work evaluated the therapeutic effect of long-term photobiomodulation (PBM) treatment with continuous-wave low-level laser on AD and its underlying mechanism. Methods: PBM was implemented for 2 min, 3 times per week for 16 months in 2-month-old transgenic AD rats. A battery of behavioral tests was performed to measure the effect of PBM treatment on cognitive dysfunction in AD rats. The effects of PBM therapy on typical AD pathologies, including amyloid plaques, intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, neuronal loss, neuronal injury, neuronal apoptosis, and neurodegeneration, were then assessed. The underlying mechanisms were measured using immunofluorescence staining, western blotting analysis, mass spectrometry, primary cortical and hippocampal cell cultures, and related assay kits. Results: PBM treatment significantly improved the typical AD pathologies of memory loss, amyloid plaques, tau hyperphosphorylation, neuronal degeneration, spine damage, and synaptic loss. PBM treatment had several mechanistic effects which may explain these beneficial effects, including 1) regulation of glial cell polarization and inhibition of neuroinflammation, 2) preservation of mitochondrial dynamics by regulating fission and fusion proteins, and 3) suppression of oxidative damage to DNA, proteins, and lipids. Furthermore, PBM enhanced recruitment of microglia surrounding amyloid plaques by improving the expression of microglial IL-3Rα and astrocytic IL-3, which implies a potential role of PBM in improving Aβ clearance. Finally, our results implicate neuronal hemoglobin in mediating the neuroprotective effect of PBM, as Hbα knockdown abolished the neuroprotective effect of PBM treatment. Conclusion: Collectively, our data supports the potential use of PBM treatment to prevent or slow the progression of AD and provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms of PBM therapy.
Keywords: Microglia recruitment; Mitochondria; Neuronal hemoglobin; Photobiomodulation; TgF344 rats.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Photobiomodulation Therapy Attenuates Anxious-Depressive-Like Behavior in the TgF344 Rat Model.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;83(4):1415-1429. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201616. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34219711
-
Long-term exercise pre-training attenuates Alzheimer's disease-related pathology in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Geroscience. 2022 Jun;44(3):1457-1477. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00534-2. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Geroscience. 2022. PMID: 35229257 Free PMC article.
-
Prodromal neuroinflammatory, cholinergic and metabolite dysfunction detected by PET and MRS in the TgF344-AD transgenic rat model of AD: a collaborative multi-modal study.Theranostics. 2021 May 3;11(14):6644-6667. doi: 10.7150/thno.56059. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34093845 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Treatment of Neurodegeneration: Integrating Photobiomodulation and Neurofeedback in Alzheimer's Dementia and Parkinson's: A Review.Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2019 Oct;37(10):623-634. doi: 10.1089/photob.2019.4685. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2019. PMID: 31647776 Review.
Cited by
-
Photobiomodulation for the treatment of neuroinflammation: A systematic review of controlled laboratory animal studies.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 20;16:1006031. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1006031. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36203812 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation Inhibits Ischemia-Induced Brain Endothelial Senescence via Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 23;13(6):633. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060633. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929072 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Hydrogen: an Emerging Therapeutic Medical Gas for Brain Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;60(4):1749-1765. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03175-w. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36567361 Review.
-
Mystery of gamma wave stimulation in brain disorders.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Dec 18;19(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00785-x. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39695746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote photobiomodulation ameliorates behavioral and neuropathological outcomes in a rat model of repeated closed head injury.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 11;15(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03228-3. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39799140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer's Association. 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17:327–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

