Combined transhepatic and transjugular approach for mechanical thrombectomy of massive TIPS thrombosis
- PMID: 35265241
- PMCID: PMC8899117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.01.086
Combined transhepatic and transjugular approach for mechanical thrombectomy of massive TIPS thrombosis
Abstract
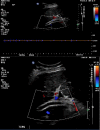
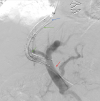
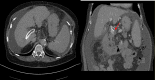
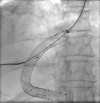
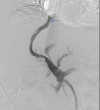
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a well-validated decompressive therapy option to manage ascites and variceal bleeding secondary to portal hypertension. Complications following TIPS procedures include hepatic encephalopathy, liver failure, and TIPS dysfunction. TIPS dysfunction is due to occlusion or stenosis of the TIPS shunt and can be caused by acute or chronic thrombosis. TIPS thrombosis is often treated with mechanical thrombectomy or catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy. Most cases of in-stent occlusion can be treated via a transjugular approach with recanalization or placement of additional stents. We present a case of a 72-year-old female who presented with worsening ascites 17 months after initial TIPS procedure; she was found to have a large thrombus completely occluding the TIPS stent. In our case, a combined transhepatic and transjugular approach was required for TIPS revision given the extent of well-organized clot located near the hepatic venous end of the stent, resulting from prolonged stent occlusion. This was an extremely challenging scenario with two overlapping covered stents and a bare metal stent at the hepatic venous end in the setting of chronic thrombosis and a well-organized fibrous cap. The case highlights the need for optimal initial placement of the primary TIPS shunt to avoid the need for subsequent complex interventions to maintain TIPS shunt patency.
Keywords: Portal hypertension; TIPS; Thrombectomy; Thrombolysis; Thrombosis; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applications of percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and portal vein thrombosis.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Mar;6(1):59-69. doi: 10.1053/tvir.2003.36433. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003. PMID: 12772131 Review.
-
[Comparison of the curative effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent and drug combined with gastroscopy as the secondary prevention of esophageal -gastric variceal bleeding in portal hypertension].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Aug 20;28(8):672-678. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20190723-00266. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32911906 Chinese.
-
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in Patients with Portal Hypertension: Patency Depends on Coverage and Interventionalist's Experience.Dig Dis. 2018;36(3):218-227. doi: 10.1159/000486030. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Dig Dis. 2018. PMID: 29316565
-
A method for revision of a foreshortened transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) stent using transhepatic trans-stent access.Radiol Case Rep. 2021 Jul 1;16(9):2376-2381. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.06.019. eCollection 2021 Sep. Radiol Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34306285 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the era of the stent graft - What the interventionists need to know?Eur J Radiol. 2021 Nov;144:109986. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109986. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34619618 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent TIPS dysfunction and variceal bleeding: A combined, staged, use of large-bore aspiration thrombectomy and partial splenic artery embolization-A case report.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Oct 30;20(1):352-356. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.10.003. eCollection 2025 Jan. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39525906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bureau C, Garcia Pagan JC, Layrargues GP, et al. Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluoroethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomized multicentre study. Liver Int. 2007;27(6):742. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

