Paediatric pneumonia research priorities in the context of COVID-19: An eDelphi study
- PMID: 35265333
- PMCID: PMC8874896
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.12.09001
Paediatric pneumonia research priorities in the context of COVID-19: An eDelphi study
Abstract
Background: Pneumonia remains the leading cause of infectious deaths in children under-five globally. We update the research priorities for childhood pneumonia in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and explore whether previous priorities have been addressed.
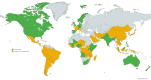
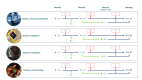
Methods: We conducted an eDelphi study from November 2019 to June 2021. Experts were invited to take part, targeting balance by: gender, profession, and high (HIC) and low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). We followed a three-stage approach: 1. Collating questions, using a list published in 2011 and adding newly posed topics; 2. Narrowing down, through participant scoring on importance and whether they had been answered; 3. Ranking of retained topics. Topics were categorized into: prevent and protect, diagnosis, treatment and cross-cutting.
Results: Overall 379 experts were identified, and 108 took part. We started with 83 topics, and 81 further general and 40 COVID-19 specific topics were proposed. In the final ranking 101 topics were retained, and the highest ranked was to "explore interventions to prevent neonatal pneumonia". Among the top 20 topics, epidemiological research and intervention evaluation was commonly prioritized, followed by the operational and implementation research. Two COVID-19 related questions were ranked within the top 20. There were clear differences in priorities between HIC and LMIC respondents, and academics vs non-academics.
Conclusions: Operational research on health system capacities, and evaluating optimized delivery of existing treatments, diagnostics and case management approaches are needed. This list should act as a catalyst for collaborative research, especially to meet the top priority in preventing neonatal pneumonia, and encourage multi-disciplinary partnerships.
Copyright © 2022 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors completed the ICMJE Unified Competing Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author), and declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brown R, Head M. on behalf of The Research Investments in Global health Study. Sizing up pneumonia research: assessing global investments in pneumonia research 2000-2015. Southampton: University of Southampton; 2018.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). GBD Compare Data Visualization Seattle, Washington, USA2020. Available: http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare. Accessed: 29 July 2021.
-
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/. Accessed: 28 December 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
